ALGEBRA AND ANGLE MEASURES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Algebra can be used to find unknown values in angles using appropriate theorems and postulates in geometry.
Example 1 :
If m∠1 = 3x + 15, m∠2 = 4x - 5, and m∠3 = 5y, find the value of x and y.
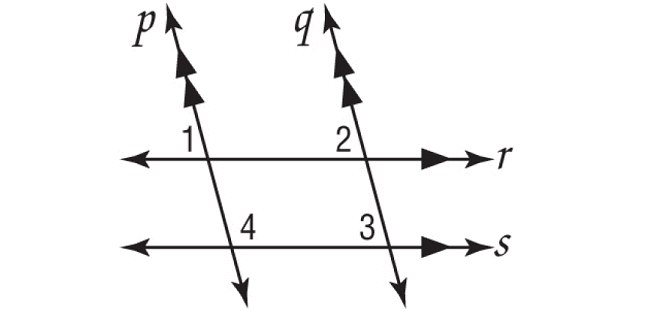
Solution :
m∠1 and m∠2 are corresponding angles and they are equal.
m∠1 = m∠2
3x + 15 = 4x - 5
Subtract 3x from each side.
15 = x - 5
Add 5 to each side.
20 = x
m∠2 and m∠3 are corresponding angles and they are equal.
m∠2 = m∠3
4x - 5 = 5y
Substitute x = 20.
4(20) - 5 = 5y
80 - 5 = 5y
75 = 5y
Divide each side by 5.
15 = y
Therefore,
x = 20 and y = 15
Example 2 :
In the figure shown below, find the values of x and y.
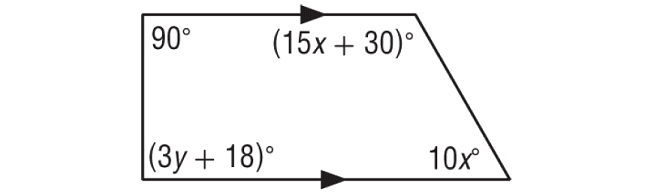
Solution :
(3y + 18)° and 90° are interior angles on the same side of the transversal and they are supplementary.
(3y + 18)° + 90° = 180°
3y + 18 + 90 = 180
3y + 108 = 180
Subtract 108 from each side.
3y = 72
Divide each side by 3.
y = 24
10x° and (15x + 30)° are interior angles on the same side of the transversal and they are supplementary.
10x° + (15x + 30)° = 180°
10x + 15x + 30 = 180
25x + 30 = 180
Subtract 180 from each side.
25x = 150
Divide each side by 25.
x = 6
Therefore,
x = 6 and y = 24
Example 3 :
In the figure shown below, find the values of x, y and z.
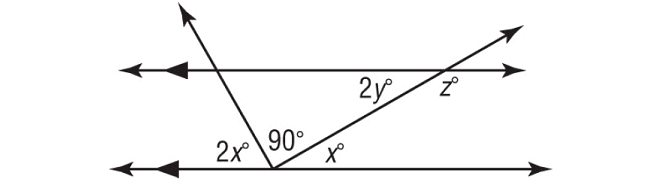
Solution :
2x°, 90° and x° together form a straight angle.
2x° + 90° + x° = 180°
3x + 90 = 180
Subtract 90 from each side.
3x = 90
Divide each side by 3.
x = 30
x° and 2y° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
2y° = x°
2y = x
Substitute x = 30.
2y = 30
Divide each side by 2.
y = 15
2y° and z° form a linear pair, they are supplementary.
2y° + z° = 180°
2y + z = 180
Substitute y = 15.
2(15) + z = 180
30 + z = 180
Subtract 30 from each side.
z = 150
Therefore,
x = 30, y = 15 and z = 150
Example 4 :
In the figure shown below, find the values of x and y.
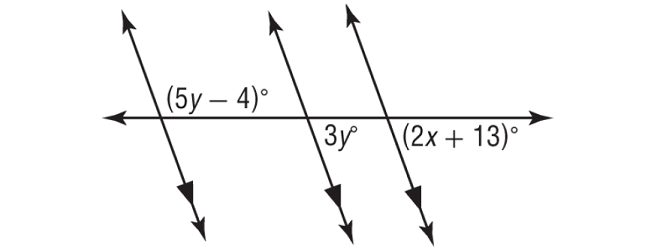
Solution :
Mark a new angle a°.
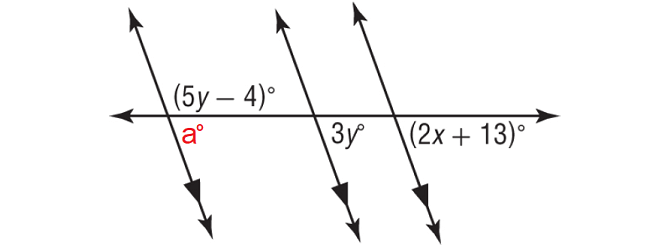
a° and (5y - 4)° form a linear pair.
a° + (5y - 4)° = 180°
a° and 3y° are corresponding angles, then a° = 3y°.
3y° + (5y - 4)° = 180°
3y + 5y - 4 = 180
8y - 4 = 180
Add 4 to each side.
8y = 184
Divide each side by 8.
y = 23
3y° and (2x + 13)° are corresponding angles and they are equal.
(2x + 13)° = 3y°
2x + 13 = 3y
Substitute y = 23.
2x + 13 = 3(23)
2x + 13 = 69
Subtract 13 from each side.
2x = 56
Divide each side by 2.
x = 28
Example 5 :
Using a 3rd parallel Line – Auxiliary Line, find the value of x.
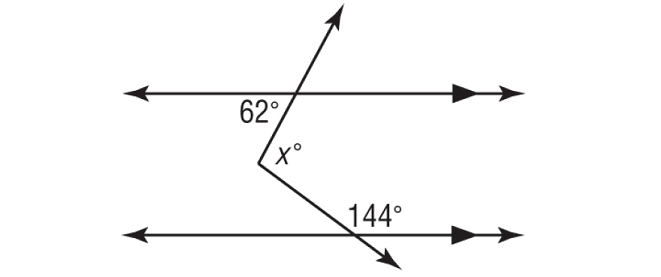
Solution :
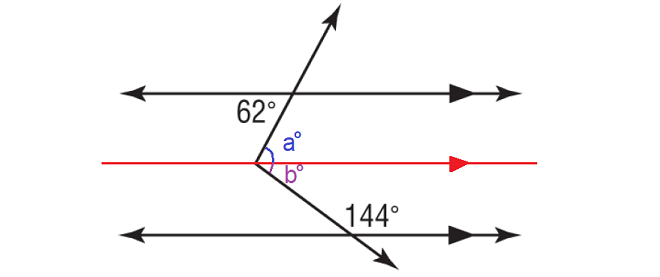
In the figure above, a° and 62° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
a° = 62°
b° and 144° are interior angles on the same side of the transversal and they are supplementary.
b° + 144° = 180°
Subtract 144° from each side.
b° = 36°
In the above figure,
x = a + b
= 62 + 36
= 98
Example 6 :
In the figure shown below, find the values of x and y.
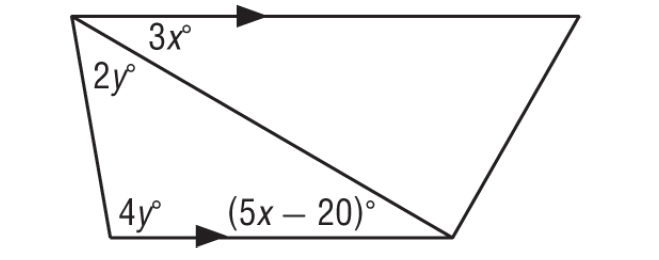
Solution :
3x° and (5x - 20)° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
3x° = (5x - 20)°
3x = 5x - 20
Subtract 3x from each side.
0 = 2x - 20
Add 20 to each side.
20 = 2x
Divide each side by 2.
10 = x
By Triangle Angle Sum Theorem,
(5x - 20)° + 2y° + 4y° = 180°
5x - 20 + 2y + 4y = 180
5x - 20 + 6y = 180
Substitute x = 10.
5(10) - 20 + 6y = 180
50 - 20 + 6y = 180
30 + 6y = 180
Subtract 30 from each side.
6y = 150
Divide each side by 6.
y = 25
Therefore,
x = 10 and y = 25
Example 7 :
In the figure shown below, find the value of x.
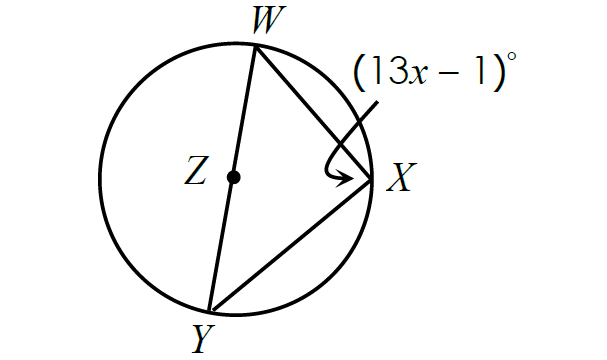
Solution :
Since the inscribed angle ∠WXY intercepts the diameter, it is a right angle.
m∠WXY = 90°
(13x - 1)° = 90°
13x - 1 = 90
Add 1 to each side.
13x = 91
Divide each side by 13.
x = 7
Example 8 :
In the figure shown below, find the value of x.
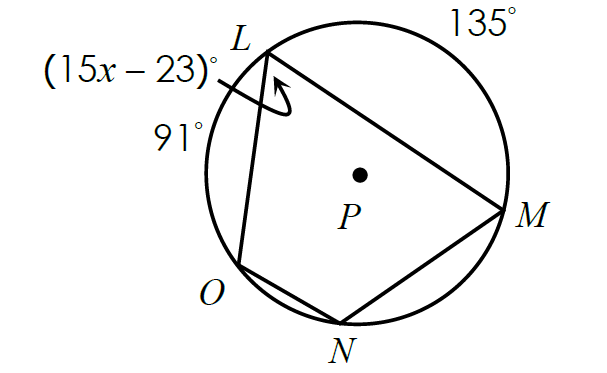
Solution :
The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half of the measure of its intercepted arc.
m∠ONM = (1/2) ⋅ m∠arc OLM
m∠ONM = (1/2) ⋅ (91° + 135°)
m∠ONM = (1/2) ⋅ 226°
m∠ONM = 113°
Since the quadrilateral LMNO is inscribed in a circle, its opposite angles are supplementary.
m∠OLM + m∠ONM = 180°
Substitute.
(15x - 23)° + 113° = 180°
15x - 23 + 113 = 180
15x + 90 = 180
Subtract 90 from each side.
15x = 90
Divide each side by 15.
x = 6
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact US | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39)
Dec 11, 25 05:59 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 38)
Dec 08, 25 12:12 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 38) -
SAT Math Practice
Dec 05, 25 04:04 AM
SAT Math Practice - Different Topics - Concept - Formulas - Example problems with step by step explanation

