ALTERNATE INTERIOR ANGLES THEOREM
Alternate Interior Angles :
When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the pair of angles formed inside the parallel lines but on the opposite sides of the transversal are called alternate interior angles.
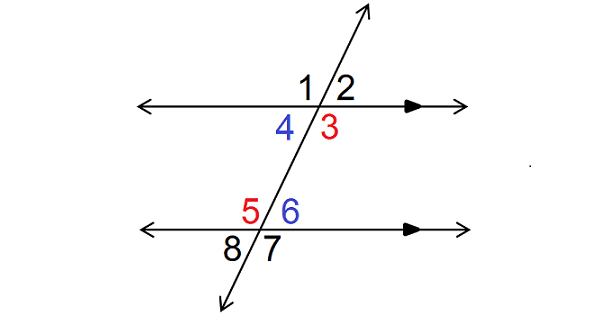
In the figure above, ∠4 and ∠6 are alternative interior angles, and also ∠3 and ∠5 are alternate interior angles.
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem :
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then Alternate Interior Angles are congruent.
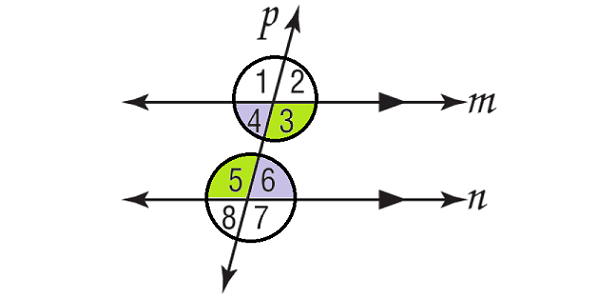
Given : m||n, p is transversal.
Prove : ∠4 and ∠6 are congruent and ∠3 and ∠5 are congruent.
Proof :
Since m || n, by the Corresponding Angles Postulate,
∠1 ≅ ∠5
By the definition of congruent angles,
m∠1 = m∠5
Since ∠5 and ∠6 form a linear pair, they are supplementary.
m∠5 + m∠6 = 180°
Substitute m∠1 for m∠5.
m∠1 + m∠6 = 180°
Subtract m∠1 from each side.
m∠6 = 180° - m∠1
m∠6 = m∠4
Therefore,
m∠4 ≅ m∠6
We can prove that m∠3 ≅ m∠5 using the same method.
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem – Converse
When two lines are cut by a transversal, if alternate interior angles have equal measure, then the two lines are parallel.
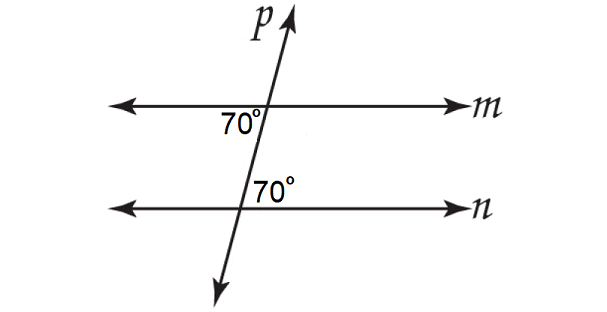
In the figure above, lines m and n are parallel. Because, a pair of alternate interior angles have equal measure.
Example 1 :
In the figure shown below, m∠8 = 75°. Find m∠3.
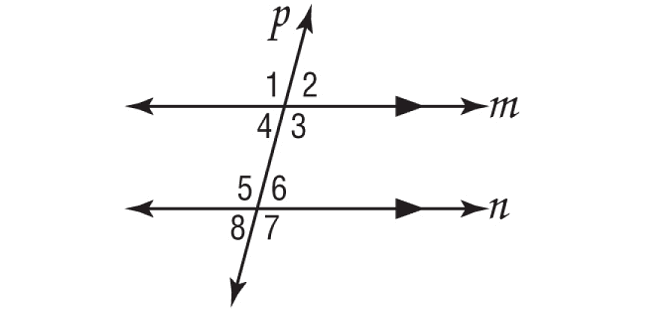
Solution :
In the figure above, lines m and n are parallel, ∠5 and ∠8 form a linear pair.
m∠5 + m∠8 = 180°
Substitute m∠8 = 75°.
m∠5 + 75° = 180°
Subtract 75° from each side.
m∠5 = 105°
∠3 and ∠5 are alternate interior angles.
∠3 ≅ ∠5
m∠3 = m∠5
Substitute m∠5 = 105°.
m∠3 = 105°
Example 2 :
In the figure shown below, m∠3 = 102°. Find the measures of ∠5, ∠11 and ∠13.
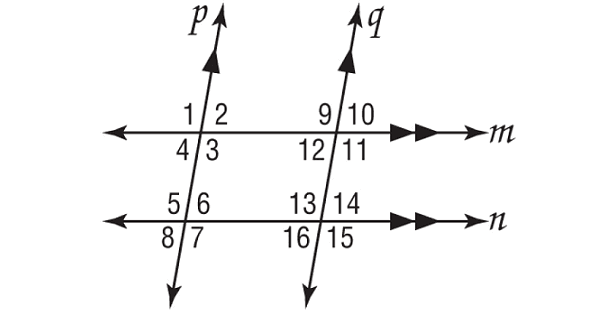
Solution :
In the figure above, lines m and n are parallel, p and q are parallel.
∠3 and ∠5 are alternate interior angles.
∠3 ≅ ∠5
m∠3 = m∠5
Substitute m∠3 = 102°.
102° = m∠5
∠5 and ∠13 are corresponding angles.
∠5 ≅ ∠13
m∠5 = m∠13
Substitute m∠5 = 102°.
102° = m∠13
∠11 and ∠13 are alternate interior angles.
∠11 ≅ ∠13
m∠11 = m∠13
Substitute m∠13 = 102°.
m∠11 = 102°
Therefore,
m∠5 = 102°
m∠11 = 102°
m∠13 = 102°
Example 3 :
In the figure shown below, lines m and n are parallel and p is transversal. Find the value of x.
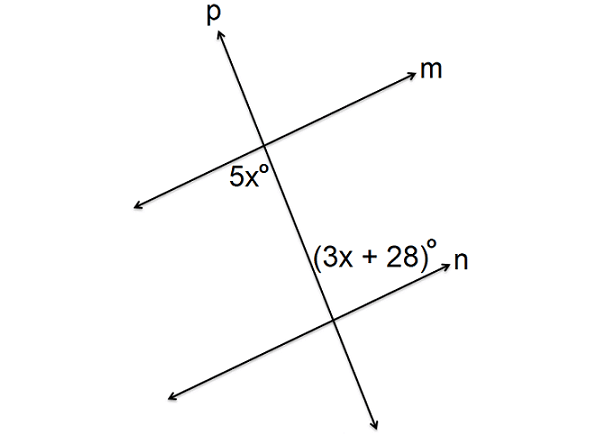
Solution :
In the figure above m and n are parallel and p is transversal. Angles 5x° and (3x + 28)° are alternate interior angles and they are congruent.
By the definition of congruent angles,
5x° = (3x + 28)°
5x = 3x + 28
Subtract 3x from each side.
2x = 28
Divide each side by 2.
x = 14
Example 4 :
Using a 3rd parallel Line – Auxiliary Line, find the value of x.
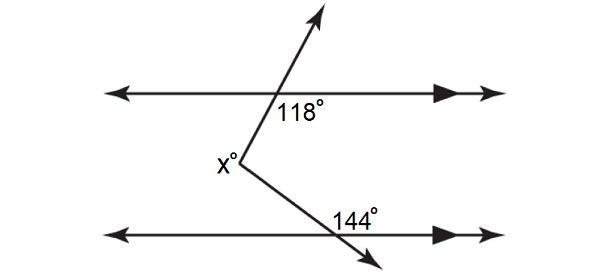
Solution :
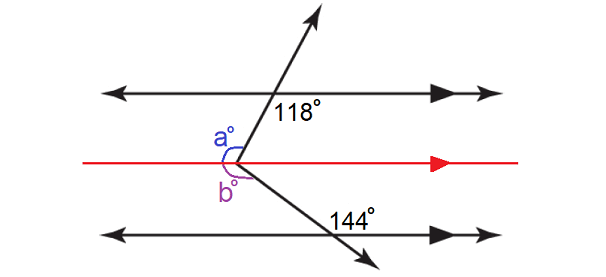
In the figure above, a° and 118° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
a° = 118°
b° and 144° are alternate interior angles and they are equal.
b° = 144°
In the figure above,
x = a + b
= 118 + 144
= 262
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19)
Apr 24, 25 11:10 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)
Apr 24, 25 11:06 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18) -
Derivative of Absolute Value of x Using Limit Definition
Apr 23, 25 11:11 AM
Derivative of Absolute Value of x Using Limit Definition