DIFFERENCE BETWEEN REFLEXIVE AND IDENTITY RELATION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Consider two sets X and Y.
Any subset of the cartesian product of X and Y is defined as a relation. In other words, a relation will be defined, when one or more elements of a set are mapped to elements of the same set or another different set.
In a cartesian product of two sets, we may define different types of relations.
In this section, we are going to discuss the two relations, reflexive and symmetric.
The two relations reflexive and identity will always appear, as if they were same.
But, there is a difference between them.
The difference between reflexive and identity relation can be described in simple words as given below.
Reflexive : Every element is related to itself
Identity : Every element is related to itself only
Let us consider an example to understand the difference between the two relations reflexive and identity.
Let R1 and R2 be two relations defined on set A---> A. That is, both the relations R1 and R2 map the elements of the set A to itself.
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, R1 and R2 be as follows.
R1 = {(1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (1,2)}
R2 = {(1,1), (2,2), (3,3)}
Reflexive Relation
In a relation, if every element of a set A is related to itself, then it is called reflexive relation.
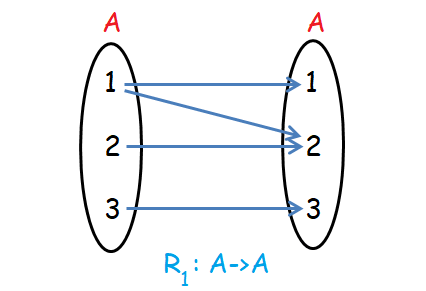
When we look at the relation R1 above, every element of A is related to itself and also, the element 1 is related to a different element 2.
More details about R1 :
(i) 1 is related to 1, 2 is related to 2 and 3 is related to 3.
(ii) Apart from 1 is related to 1, 1 is also related to 2.
Here we can not say that 1 is related to 1 only.
Because 1 is related to 2 also.
This is the point which makes the reflexive relation to be different from identity relation.
Hence R1 is reflexive relation.
Identity Relation
In a relation, if every element of a set A is related to itself only, then it is called identity relation.
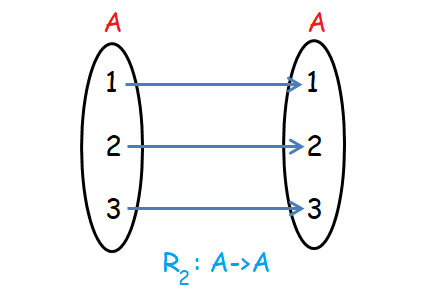
When we look at the relation R2 above, every element of A is related to itself and no element of A is related to any other different element of A.
More details about R2 :
(i) 1 is related to 1, 2 is related to 2 and 3 is related to 3.
(ii) 1 is related to 1 and it is not related to any different element. The same thing happened to 2 and 3.
From the second point, it is very clear that every element of A is related to itself only. No element of A is related to any different element.
This is the point which makes identity relation to be different from reflexive relation.
Hence R2 is identity relation.
That is,
Reflexive : Every element is related to itself
Identity : Every element is related to itself only
Solved Problems
Problem 1 :
Can every identity relation be a reflexive relation? Explain with an example.
Solution :
Yes, every identity relation is a reflexive relation
Let X = {a, b, c} and R be a relation defined on X such that
R = {(a, a), (b, b), (c, c)}
In the relation R above, every element of X is related to itself only. So, R is an identity relation. And also, R meets the condition of reflexive relation. That is, every element of X is related to itself. Therefore, R is also a relflexive relation.
Problem 2 :
Can every reflexive relation be an identity relation? Explain with an example.
Solution :
No, every reflexive relation need NOT be an identity relation.
Let Y = {p, q, r} and R be a relation defined on Y such that
R = {(p, p), (q, q), (r, r), (p, q)}
In the relation R above, every element of X is related to itself. So, R is a reflexive relation. But, R does NOT meet the condition of identity relation. That is, every element of Y is related to itself only.
In the relation R above, p is related to itself, and also p is related to a different element q.
"(p, q) or p related to q" violates the condition of identity relation, that is, "every element has to be related to itself only".
Therefore, R is NOT an identity relation.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
US Common Core K-12 Curriculum Algebra Word Problems
Dec 20, 25 01:19 AM
US Common Core K-12 Curriculum Algebra Word Problems on Systems of LInear Equations -
US Common Core K-12 Curriculum Algebra Solving Systems of Equations
Dec 20, 25 01:18 AM
US Common Core K-12 Curriculum - Algebra : Solving Systems of Linear Equations -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 40)
Dec 18, 25 06:27 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 40)
