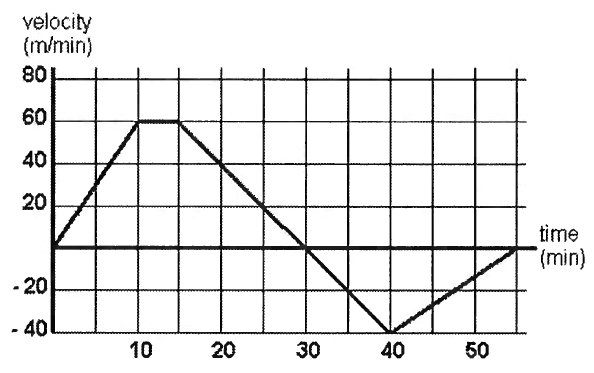
DIVIDING POLYNOMIALS BY LONG DIVISION WORKSHEET
Divide the following polynomials using long division.
Problem 1 :
(2x3 - 6x2 + 5x + 4) ÷ (x - 2)
Problem 2 :
(4x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2) ÷ (x - 1)
Problem 3 :
(x3 - 7x2 - x + 6) ÷ (x + 2)
Problem 4 :
(10- 4x + 3x2) ÷ (x - 2)

1. Answer :
(2x3 - 6x2 + 5x + 4) ÷ (x - 2)
Let P(x) = 2x3 - 6x2 + 5x + 4 and g(x) = x - 2
To divide the given polynomial by x - 2, we have divide the first term of the polynomial P(x) by the first term of the polynomial g(x).
If we divide 2x3 by x, we get 2x2. Now we have to multiply this 2x2 by x - 2. From this we get 2x3 - 4x2.
Now we have to subtract 2x3 - 4x2 from the given polynomial. So we get -2x2 + 5x + 4.
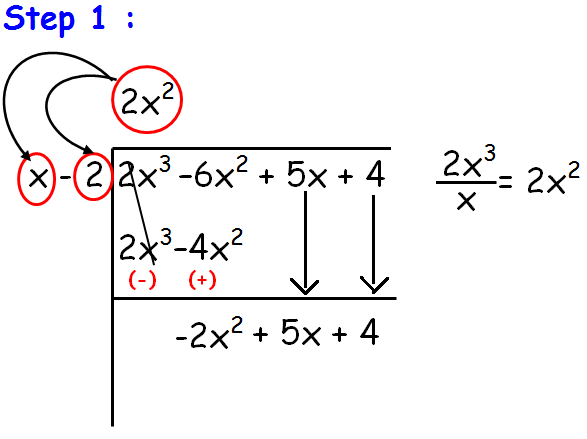
Now we have to subtract 2x3 - 4x2 from the given polynomial. So we get -2x2 + 5x + 4.
repeat this process until we get the degree of p(x) ≥ degree of g(x).
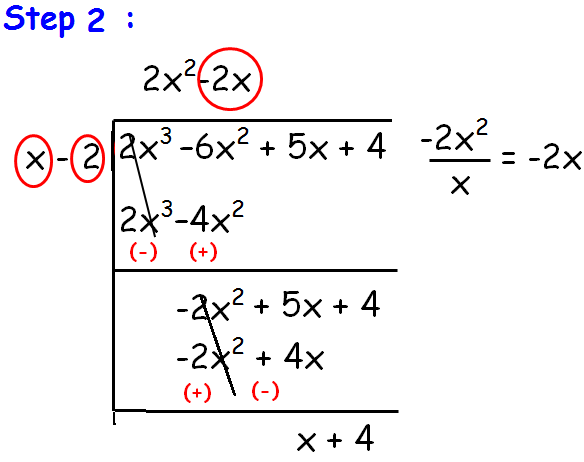
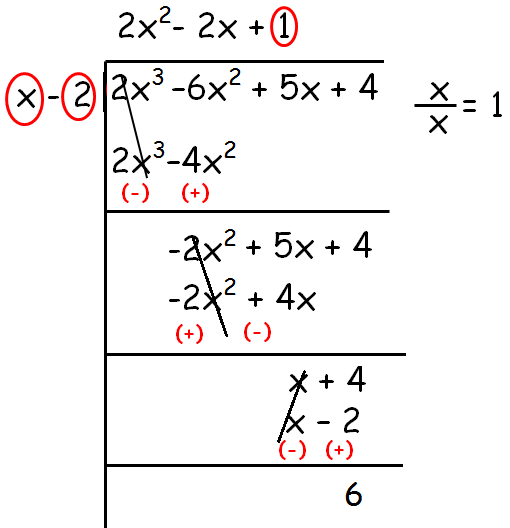
So,
Quotient = 2x2 - 2x + 1
Remainder = 6
2. Answer :
(4x3 - 5x2 + 6x - 2) ÷ (x - 1)
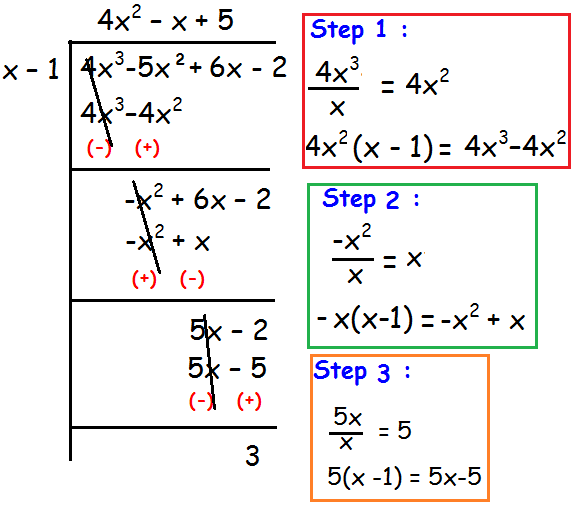
So,
Quotient = 4x2 - x + 5
Remainder = 3
3. Answer :
(x3 - 7x2 - x + 6) ÷ (x + 2)
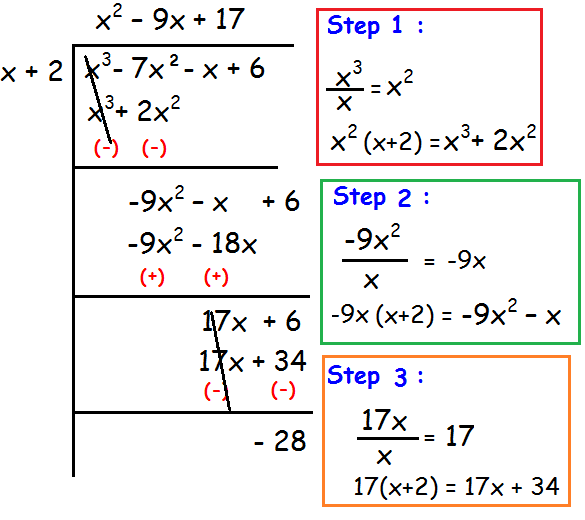
So,
Quotient = x2 - 9x + 17
Remainder = -28
4. Answer :
(10- 4x + 3x2) ÷ (x - 2)
Let us first write the terms of each polynomial in descending order ( or ascending order).
Thus, the given problem becomes (10- 4x + 3x2) ÷ (x - 2)
f(x) = 10- 4x + 3x2
= 3x2 - 4x + 10
g(x) = x - 2
Step 1 :
In the first step, we are going to divide the first term of the dividend by the first first term of the divisor.
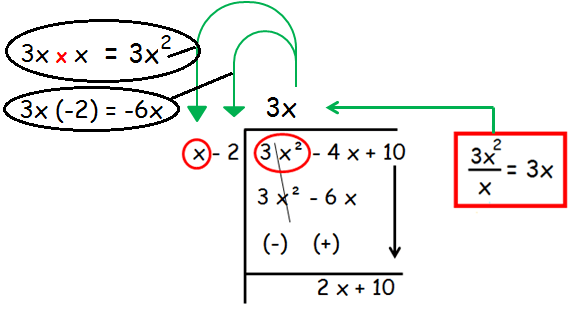
After changing the signs, +3x2 and -3x2 will get canceled. By simplifying, we get 2x + 10.
Step 2 :
In the second step again we are going to divide the first term that is 2x by the first term of divisor that is x.
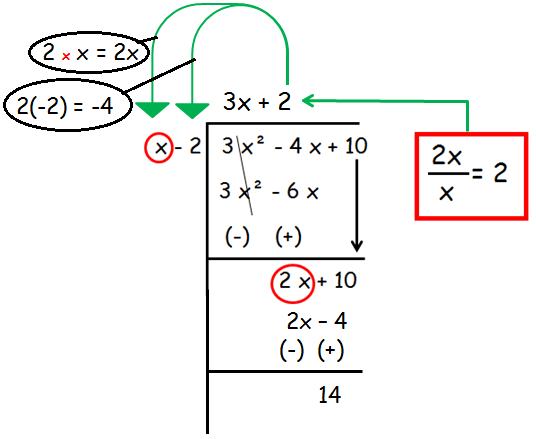
So,
Quotient = 3x + 2
Remainder = 14
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 150)
Apr 25, 25 11:46 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 150) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19)
Apr 24, 25 11:10 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)
Apr 24, 25 11:06 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)