RATIONAL EXPONENTS
We use radical symbol √ to indicate roots. The index is the small number to the left of the radical symbol that says which root has to be taken.
For example, 3√ represents a cube root. Because,
23 = 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 = 8, 3√8 = 2
Another way to write nth roots is by using exponents that are fractions.
For example, for a > 1, suppose √a = am, then
√a = am
Square both sides.
(√a)2 = (am)2
Power of a Power Property.
a1 = a2m
If two terms are equal with the same base, then the exponents must be equal.
1 = 2m
Divide each side by 2.
1/2 = m
So, for all a > 1, √a = a1/2.
Definition of a1/n :
Words :
A number raised to the power of 1/n is equal to the nth root of that number.
Numbers :
51/2 = √5
31/4 = 4√3
41/7 = 7√4
Algebra :
If a > 1 and n is an integer, where n ≥ 2, then
a1/n = n√a
And also,
a1/2 = √a
a1/3 = 3√a
a1/4 = 4√a
and so on.
Example 1 :
Simplify :
641/3
Solution :
= 641/3
Use the definition of a1/n.
= 3√64
= 3√(43)
= 4
Example 2 :
Simplify :
811/4
Solution :
= 811/4
Use the definition of a1/n.
= 4√81
= 4√(34)
= 3
Example 3 :
Simplify :
321/5 + 1001/2
Solution :
= 321/5 + 1001/2
Use the definition of a1/n.
= 5√32 + √100
= 5√(25) + √(102)
= 2 + 10
= 12
Example 4 :
Simplify :
1211/2 + 2561/4
Solution :
= 1211/2 + 2561/4
Use the definition of a1/n.
= √121 + 4√256
= √(112) + 4√(44)
= 11 + 4
= 15
Numerator Other than 1
A fractional exponent can have a numerator other than 1, as in the expression b2/3.
You can write the exponent as a product in two different ways as shown below.
|
b2/3 = b(1/3) ⋅ 2 = (b1/3)2 = (3√b)2 |
b2/3 = b2 ⋅ 1/3 = (b2)1/3 = 3√(b2) |
Definition of am/n :
Words :
A number raised to the power of m/n is equal to the nth root of the number raised to mth power.
Numbers :
82/3 = (3√8)2 = 22 = 4
or
82/3 = 3√(82) = 3√64 = 4
Algebra :
If a > 1 and m and n are integers, where n ≥ 1 and n ≥ 2, then
am/n = (n√a)m = n√(am)
Example 5 :
Simplify :
2162/3
Solution :
= 2162/3
Use the definition of am/n.
= (3√216)2
= (3√63)2
= (6)2
= 36
Example 6 :
Simplify :
324/5
Solution :
= 324/5
Use the definition of am/n.
= (5√32)4
= (5√25)4
= (2)4
= 16
Example 7 :
Simplify :
274/3
Solution :
= 274/3
Use the definition of am/n.
= (3√27)4
= (3√33)4
= (3)4
= 81
Note :
Remember that √ always indicate a nonnegative square root. When you simplify variable expressions that contain √, such as √x2, the answer can not be negative. But x may be negative. Therefore you simplify √x2 as |x| to ensure the answer is nonnegative.
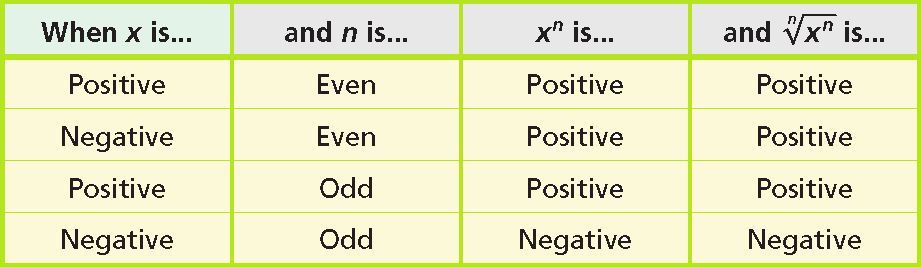
When n is even, you must simplify n√xn, to |x|, because you do not know whether x is positive or negative. When n is odd, simplify n√xn, to x.
n√xn = |x|, when n is even
n√xn = x, when n is odd
Example 8 :
Simplify :
3√(x9y3)
Solution :
= 3√(x9y3)
Use the definition of am/n.
= (x9y3)1/3
Power of a Product Property.
= (x9)1/3 ⋅ (y3)1/3
Power of a Power Property.
= (x9 ⋅ 1/3) ⋅ (y3 ⋅ 1/3)
Simplify exponents.
= (x3) ⋅ (y1)
= x3y
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 134)
Apr 02, 25 12:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 134) -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Apr 02, 25 12:35 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part 135)
Apr 02, 25 12:32 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part 135)