FIND ANGLES OF ISOSCELES TRIANGLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
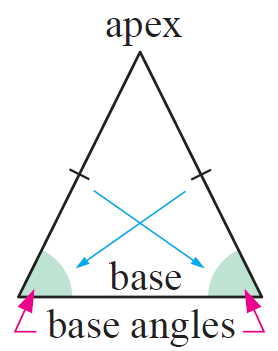
An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which two sides are equal in length.
The two sides which are having equal measures will have equal angles.
Example 1 :
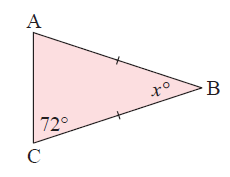
Solution :
Since AB = BC, <C = <A
The Sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180˚
So, <A + <B + <C = 180˚
72˚+x˚+72˚ = 180˚
144˚+x˚ = 180˚
x = 36˚
<B = 36˚
So, the missing angle x is 36˚.
Example 2 :
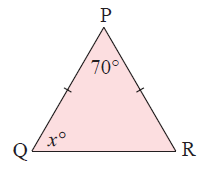
Solution :
Since PQ = PR, <PQR = <PRQ = x
So, <P + <Q + <R = 180˚
70˚ + x˚ + x˚ = 180˚
70˚ + 2x˚ = 180˚
2x˚ = 180˚ - 70˚
x = 110/2
x = 55˚
<Q = <R = 55˚
<Q = 55˚ and <R = 55˚
So, the missing angle x is 55˚
Example 3 :
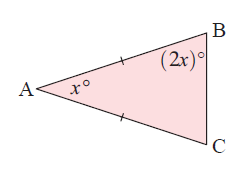
Solution :
Since AB = AC, <B = <C
<B = <C = (2x)˚
The Sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180˚
So, <A + <B + <C = 180˚
x˚ + 2x˚ + 2x˚ = 180˚
x˚ + 4x˚ = 180˚
5x˚ = 180˚
x˚ = 180/5
x = 36˚
So, the missing angle x is 36˚
Example 4 :
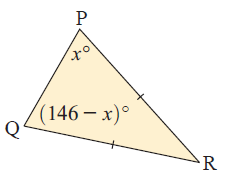
Since RQ = RP
<P
= <Q
x˚ = (146 – x)˚
x = 146 – x
x + x = 146
2x = 146
x = 146/2
x = 73˚
So, the missing angle x is 73˚.
Example 5 :
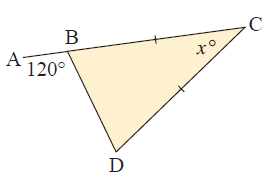
Solution :
<B = <D
<DBC + <DBA = 180˚ (linear pair of angles)
<DBC + 120˚ = 180˚
<DBC = 180˚-120˚
<DBC = 60˚
<B = 60˚
<B = <D = 60˚
The Sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180˚
<C + <B + <D = 180˚
x˚ + 60˚ + 60˚ = 180˚
x˚ + 120˚ = 180˚
x = 180˚ - 120˚
x = 60˚
So, the missing angle x is 60˚.
Example 6 :
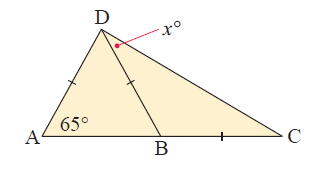
Solution :
Since AD = DB, ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle.
DB = BC, ∆DBC is an isosceles triangle.
<DAB = <DBA = 65
<DBA + <DBC = 180
65 + <DBC = 180
<DBC = 115
In triangle DBC.
Let x be <BCD and <CDB
<DBC + <BCD + <CDB = 180
115 + x + x = 180
2x = 180-115
2x = 65
x = 32.5
Example 7 :
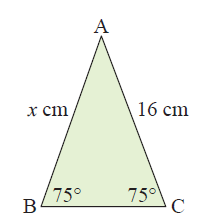
Solution :
Since <B = <C = 75˚
AB = x cm, AC = 16 cm
AB
= AC
x = 16 cm
Example 8 :
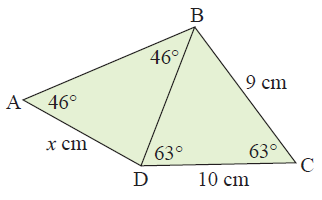
Solution :
|
In triangle ADB <DAB = <DBA = (46˚) |
In triangle BDC BD = BC (9 cm) |
DA = DB
BD = 9 cm
So,
x = BD
x = 9 cm and DA = 9 cm
Example 9 :

Solution :
∆ABC is an isosceles triangle (AB = AC).
base <B = <C are equal.
M is the midpoint of the angle bisects the base at right angles.
<AMC = <AMB = 90˚
x = 90˚
Example 10 :
The figure alongside has not been drawn accurately:
a) Find x.
b) What can be deduced about the triangle?
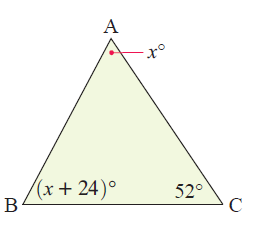
Solution :
(a) <A + <B + <C = 180
x + x + 24 + 52 = 180
2x + 76 = 180
2x = 104
x = 52
(b) In the above triangle, two angles are equal. So it is isosceles triangle.
Example 11 :
The degree measure of the vertex angle is (7x - 27). The degree measure for each base is (9x - 34) . What is the value of one base angle?
Solution :
Vertex angle = 7x - 27
One base angle = 9x - 34
Other base angle will also be the same.
7x - 27 + 2(9x - 34) = 180
7x - 27 + 18x - 68 = 180
25x - 95 = 180
25x = 180 + 95
25x = 275
x = 275/25
x = 11
Applying this value in 9x - 34
= 9(11) - 34
= 99 - 34
= 65 degree
Example 12 :
The ratio of the measure of a base angle in an isosceles triangle to the measure of the vertex angle is 2:16. Find the measure of each angle.
Solution :
Let base angles be 2x and vertex angle be 16x
2x + 2x + 16x = 180
4x + 16x = 180
20x = 180
x = 180/20
x = 9
2x = 2(9) ==> 18
16x = 16(9) = 144
So, the required angles are 18, 18 and 144.
Example 13 :
The degree measure of the vertex angle is (x + 21). The degree measure for each base is (2x + 17) . What is the value of x?
Solution :
Vertex angle = x + 21
Base angle = 2x + 17
x + 21 + 2(2x + 17) = 180
x + 21 + 4x + 34 = 180
5x + 55 = 180
5x = 180 - 55
5x = 125
x = 125/5
x = 25
So, the value of x is 25.
Example 14 :
The vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is 76 . The degree measure for each base . What is the measure of one base angle?
Solution :
The vertex angle = 76
Measure of each base = x
x + x + 76 = 180
2x = 180 - 76
2x = 104
x = 104/2
x = 52
Example 15 :
The ratio of the measure of a base angle in an isosceles triangle to the measure of the vertex angle is 1:7. Find the measure of each angle.
Solution :
The ratio between base angle and vertex angle is 1 : 7, then the angles are x and 7x
x + x + 7x = 180
9x = 180
x = 180/9
x = 20
Each angles are 20, 20 and 140.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact US | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39)
Dec 11, 25 05:59 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 38)
Dec 08, 25 12:12 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 38) -
SAT Math Practice
Dec 05, 25 04:04 AM
SAT Math Practice - Different Topics - Concept - Formulas - Example problems with step by step explanation

