FIND AREA BETWEEN TWO CURVES EXAMPLES
Consider the region S that lies between two curves y = f(x) and y = g(x) and between the vertical lines x = a and x = b, where f and g are continuous functions and f(x) ≥ g(x) for all in x [a, b].
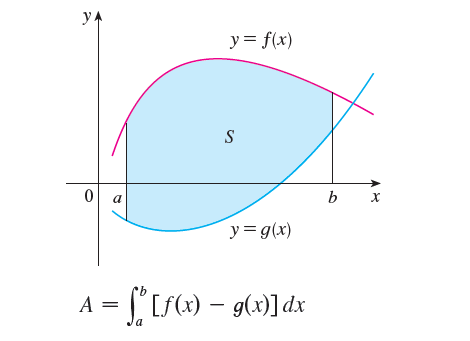
Example 1 :
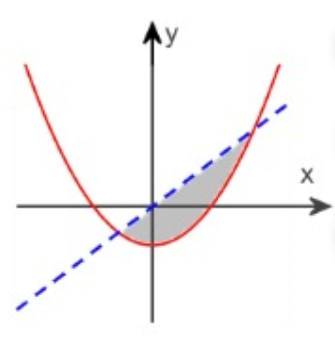
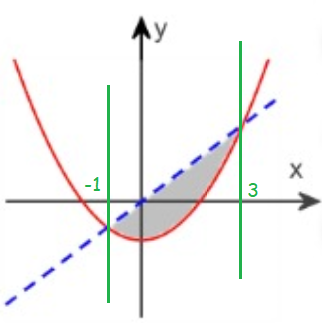
In the figure given below, the equation of the solid parabola is y = x2 - 3 and the equation of the dashed line is y = 2x. Determine the area of the shaded region.
Solution :
Let us find the point of intersection,
y = x2 - 3 ----(1)
y = 2x ----(2)
(1) = (2)
x2 - 3 = 2x
x2 - 2x - 3 = 0
(x - 3) (x + 1) = 0
x = 3 and x = -1
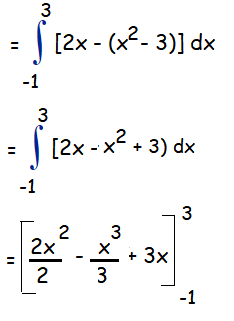
= [9 - (27/3) + 9] - [1 + (1/3) - 3]
= 9 - (3 + 1 - 9)/3
= 9 + (5/3)
= (27 + 5)/3
= 32/3
So, the required area is 32/3.
Example 2 :
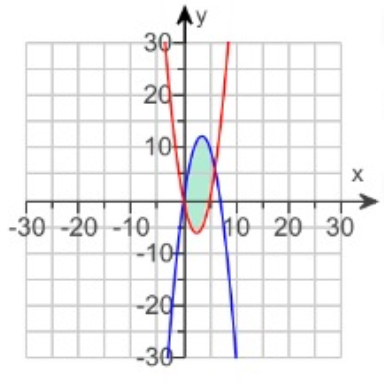
Determine the area of the shaded region bounded by
y = -x2 + 7x and y = x2 - 5x
Solution :
y = -x2 + 7x -----(1)
y = x2 - 5x -----(2)
(1) = (2)
-x2 + 7x = x2 - 5x
-2x2 = -5x - 7x
-2x2 = -12x
x2 - 6x = 0
x(x - 6) = 0
x = 0 and x = 6
The x-coordinates of point of intersection of the above curves are 0 and 6..
To find the required area, we should subtract the area below the parabola which is open upward from the area of the below the parabola which is open downward.
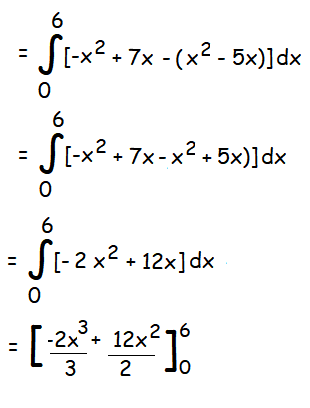
= -2(216)/3 + 6(36) - 0
= (-512/3) + 216
= (-512 + 648)/3
= 136/3
Example 3 :
In the graph given below, the equation of the parabola is
x = (y-2)2/2
and the equation of the line
y = 6-x.
Determine the area of the shaded region.
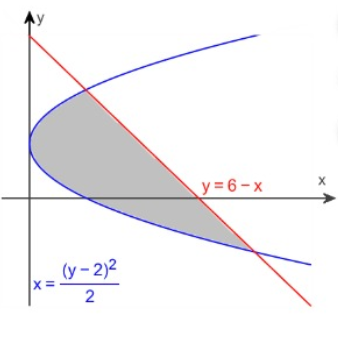
x = (y - 2)2/2 ----(1)
x = 6 - y ----(2)
(1) = (2)
(y - 2)2/2 = 6 - y
(y - 2)2 = 2(6 - y)
y2 - 4y + 4 = 12 - 2y
y2 - 2y - 8 = 0
(y - 4) (y + 2) = 0
y = 4 and y = -2
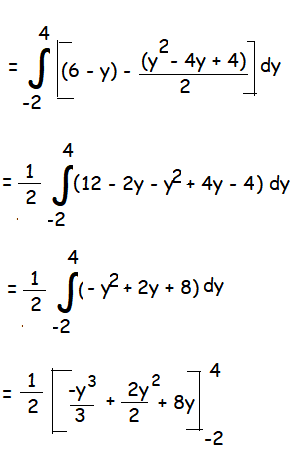
= (1/2) [(-64/3 + 16 + 32) - (8 + 4 - 16)]
= (1/2) [(-64/3 + 48) - (-4)]
= (1/2) (-64/3 + 52)
= (1/2)[(-64 + 156)/3]
= (1/2)(92/3)
= 31/3
Example 4 :
Example 4 :
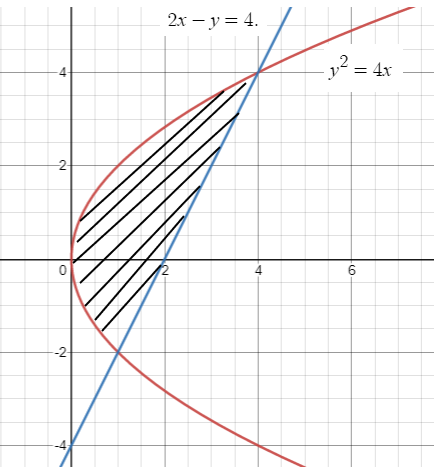
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola
y2 = 4x
and the line
2x-y = 4
Solution :
To find the point of intersection, we have to solve the equations.
x = y2/4 ------ (1)
x = (4+y)/2 ------ (2)
(1) = (2)
y2/4 = (4 + y)/2
2y2 = 4(4 + y)
2 y2 = 16 + 4 y
2y2-4y-16 = 0
now we are going to divide the whole equation by 2,
y2-2y-8 = 0
(y-4) (y+2) = 0
y-4 = 0 y+2 = 0
y = 4 y = -2
Point of intersection of two curves are (0, 4) (0, -2).
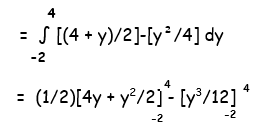
= [(32+16)/4 - (64/12) ] - [ (-16 + 4)/4 - (-8/12) ]
= [(48/4) - (16/3)] - [(-12/4) - (-8/12)]
= [12-(16/3)] - [-3 + (2/3)]
= [(36-16)/3)] - [(-9+2)/3]
= [20/3] - [-7/3]
= (20/3) + (7/3)
= (20+7)/3
= 27/3
= 9 square units
Example 5 :
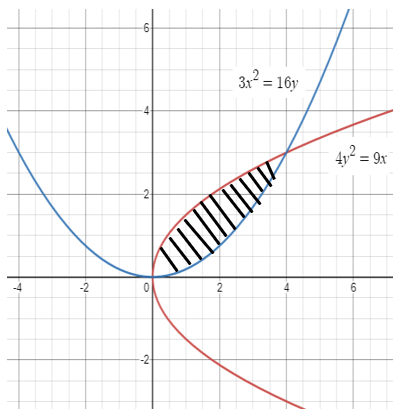
Find the common area enclosed by the parabolas
4y2 = 9x
and
3x2 = 16y
Solution :
4y2 = 9x ---(1)
3x2 = 16y ---- (2)
y = (3 √x)/2
y = 3x2/16
y = y
(3√x)/2 = 3x2/16
48 √x = 6x2
(48/6)√x = x²
8 √x = x2
√x = x2/8
taking squares on both sides
x = x4/64
64 = x4/x
64 = x3
43 = x3
x = 4
y = 3 (4)2/16
y = 3
Point of intersection are (0, 0) and (4, 3).
To find the required area that is shaded portion, we have to subtract the area which is open upward from the area which is open rightward.
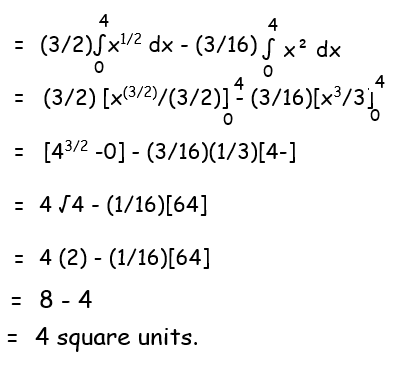
Example 6 :
Find the area of the circle whose radius is a
Solution :
Equation of circle :
x2 + y² = a2
y2 = a2-x2
y = √(a2-x2)
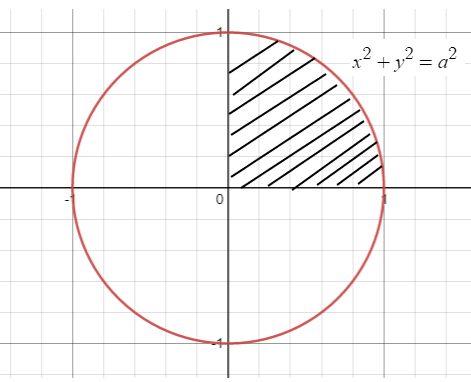
Required area = 4 integral to 0 to a √(a² - x²) dx
= 4 [(x/2)√(a² - x²) + a²/2 sin⁻¹ (X/a)]
= 4[(a/2)√(a² - a²) + (a²/2) sin⁻¹ (a/a)] - 0 - 0]
= 4[0 + (a²/2) sin⁻¹ (1)]
= 4[0 + (a²/2) (π/2)]
= 4[(πa²/4)]
= π a² square units
Therefore the required area of circle is πa² square units.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146)
Apr 18, 25 06:52 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146) -
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions
Apr 16, 25 09:25 PM
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)
Apr 16, 25 12:35 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)