FIND COMPOSITION OF TWO FUNCTIONS
Definition :
Let f : A ----> B and g : B ----> C be two functions. Then the composition of f and g denoted by g o f is defined as the function g o f(x) = g[f(x)] for all x ∈ A.
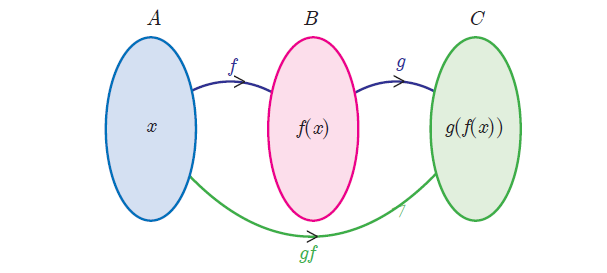
Note :
Generally, f o g ≠ g o f for any two functions f and g. So, composition of functions is not commutative.
Example 1 :
Find f o g, if f(x) = x and g(x) = 3x2.
Solution :
f o g = f[g(x)]
= f[3x2]
= 3x2
Example 2 :
If f(x) = 2x - 5 and g(x) = x + 2 find f o g.
Solution :
f o g = f[g(x)]
= f[x + 2]
= 2(x + 2) - 5
= 2x + 4 - 5
= 2x - 1
Example 3 :
If f(x) = -3x + 4 and g(x) = x2 find g o f.
Solution :
g o f = g[f(x)]
= g[-3x + 4]
= (-3x + 4)2
= (-3x)2 + 2(-3x)(4) + 42
= 9x2 - 24x + 16
Example 4 :
If f(x) = 4x2 + 2 and g(x) = √(x- 8) find f o g.
Solution :
f o g = f[g(x)]
= f[√(x- 8)]
= 4[√(x- 8)]2 + 2
= 4(x- 8) + 2
= 4x - 32 + 2
= 4x - 30
Example 5 :
If f(x) = -9x + 4 and g(x) = x4, find g o f.
Solution :
g o f = g[f(x)]
= g[-9x + 4]
= (-9x + 4)4
Example 6 :
If f(x) = 2x + 1 and g(x) = x2 - 2, then verify f o g = g o f.
Solution :
f o g :
= f[g(x)]
= f[x2 - 2]
= 2(x2 - 2) + 1
= 2x2 - 4 + 1
= 2x2 - 3 ----(1)
g o f :
= g[f(x)]
= g[2x + 1]
= (2x + 1)2 - 2
= (2x)2 + 2(2x)(1) + 12 - 2
= 4x2 4x + 1 - 2
= 4x2 4x - 1 ----(2)
From (1) and (2), we see that f o g ≠ g o f.

Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in Math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 100)
Jan 14, 25 12:34 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 100) -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Jan 14, 25 12:23 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Best Way to Learn Mathematics
Jan 12, 25 11:03 PM
Best Way to Learn Mathematics