FIND THE VALUE OF K IN THE QUADRATIC EQUATION
Quadratic equation :
The standard form of quadratic equation is
ax2 + bx + c = 0
(where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0)
We can find the roots of the quadratic equation using the formula,
x = [-b ± √(b2 - 4ac)]/2a
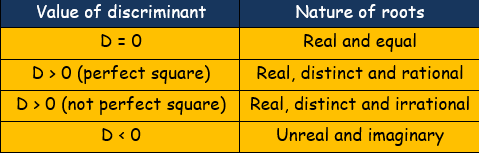
Here, b2 - 4ac called as the discriminant (which is denoted by D) of the quadratic equation, decides the nature of roots as follows.
D = b2 – 4ac
Find values of k such that :
Example 1 :
kx2 + 12x + 2 = 0 has a repeated root
Solution :
Given, kx2 + 12x + 2 = 0
By comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 in the given equation, we get
Here, a = k, b = 12, and c = 2
Since the roots are real and equal, then D = 0
b2 – 4ac = 0
(12)2 – 4(k)(2) = 0
144 – 8k = 0
-8k = -144
k = 144/8
k = 18
So, the value of k is 18
Example 2 :
3x2 + 16x + k = 0 has a repeated root
Solution :
Given, 3x2 + 16x + k = 0
By comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 in the given equation, we get
Here, a = 3, b = 16, and c = k
Since the roots are real and equal, then D = 0
b2 – 4ac = 0
(16)2 – 4(3)(k) = 0
256 – 12k = 0
-12k = -256
k = (256)/12
k = 64/3
By writing a mixed fraction, we get
k = 21 1/3
So, the value of k is 21 1/3
Example 3 :
kx2 + 6x - 3 = 0 has two distinct real roots
Solution :
Given, kx2 + 6x - 3 = 0
By comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 in the given equation, we get
Here, a = k, b = 6, and c = -3
Since the roots are real and distinct, then D > 0
b2 – 4ac > 0
(6)2 – 4(k)(-3) > 0
36 + 12k > 0
12k > -36
k > -36/12
k > -3
So, the solution of k is k > -3, k ≠ 0
Example 4 :
4x2 - 12x + k = 0 has two distinct real roots
Solution :
Given, 4x2 - 12x + k = 0
By comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 in the given equation, we get
Here, a = 4, b = -12, and c = k
Since the roots are real and equal, then D > 0
b2 – 4ac > 0
(-12)2 – 4(4)(k) > 0
144 – 16k > 0
-16k > -144
k < (144)/16
k < 9
So, the solution of k is k < 9
Example 5 :
2x2 - 5x + k = 0 has no real solutions
Solution :
Given, 2x2 - 5x + k = 0
By comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 in the given equation, we get
Here, a = 2, b = -5, and c = k
Since the roots are not real, then D < 0
b2 – 4ac < 0
(-5)2 – 4(2)(k) < 0
25 – 8k < 0
-8k < -25
k > 25/8
By writing a mixed fraction, we get
k > 3 1/8
So, the solution of k is k > 3 1/8
Example 6 :
kx2 - 11x - k = 0 has no real roots.
Solution :
Given, kx2 - 11x - k = 0
By comparing ax2 + bx + c = 0 in the given equation, we get
Here, a = k, b = -11, and c = -k
Since the roots are not real, then D < 0
b2 – 4ac < 0
(-11)2 – 4(k)(-k) < 0
121 + 4k2 < 0
4k2 < -121
k2 < -(121/4)
k < √(-121/4)
Since we have a root that is imaginary, so there is no solution.
Example 7 :
The value of k for which x = -2 is a root of the quadratic equation kx2 + x - 6 = 0.
Solution :
kx2 + x - 6 = 0
Since -2 is a root of the polynomial, then
k(-2)2 + (-2) - 6 = 0
4k - 2 - 6 = 0
4k - 8 = 0
4k = 8
k = 8/4
k = 2
So, the required value of k is 2.
Example 8 :
px2 + 3x + q = 0 has two roots x = -1 and x = -2, then the value of p - q is.
Solution :
Given quadratic equation is,
px2 + 3x + q = 0
When x = -1
p(-1)2 + 3(-1) + q = 0
p - 3 + q = 0
p + q = 3 ------(1)
When x = -2
p(-2)2 + 3(-2) + q = 0
4p - 6 + q = 0
4p + q = 6 ------(2)
(1) - (2)
p + q - 4p - q = 3 - 6
-3p = -3
p = 1
Applying the value of p, we get
1 + q = 3
q = 3 - 1
q = 2
p - q = 1 - 2
= -1
So, the answer is -1.
Example 9 :
The value of p so that the quadratic equation
x2 + 5px + 16 = 0
has no real root is
a) p > 8 b) p < 5 c) -8/5 < p < 8/5 d) -8/5 ≤ x < 0
Solution :
x2 + 5px + 16 = 0
Since the quadratic equation has no real roots, then
b2 - 4ac < 0
a = 1, b = 5p and c = 16
(5p)2 - 4(1)(16) < 0
25p2 - 64 < 0
25p2 < 64
p2 < 64/25
p < ±8/5
-8/5 < p < 8/5
So, option c is correct.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Eliminating the Parameter in Parametric Equations
Apr 21, 25 10:37 PM
Eliminating the Parameter in Parametric Equations -
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 3)
Apr 21, 25 02:37 AM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 3) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 147)
Apr 20, 25 08:38 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 147)