FINDING LINEAR APPROXIMATION FOR A FUNCTION
Let f : (a,b)→R be a differentiable function and
x0 ∈ (a, b)
We define the linear approximation L of f at x0 by
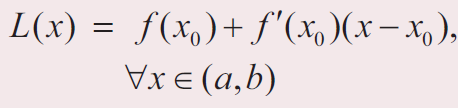
Find a linear approximation for the following functions at the indicated points.
Problem 1 :
f(x) = x3-5x+12 and x0 = 2
Solution :
f(x) = x3-5x+12
Let x0 = 2
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x - x0)
|
f(x) = x3-5x+12 f(x0) = 23-5(2)+12 f(2) = 8-10+12 f(2) = 10 |
f(x) = x3-5x+12 f'(x) = 3x2-5 f'(x0) = 3x2-5 f'(2) = 3(2)2-5 f'(2) = 12-5 f'(2) = 7 |
L(x) = f(2) + f'(2) (x - 2) ----(1)
Applying the above values in (1), we get
L(2) = 10 + 7(x - 2)
L(2) = 10 + 7x - 14
L(2) = 7x - 4
Problem 2 :
g(x) = √(x2+9) and x0 = -4
Solution :
g(x) = √(x2+9) and x0 = -4
Here f(x) and g(x) are equal.
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0) ----(1)
g(x0) = √((-4)2+9) = √(42+9) = 5
g'(x) = [1/2√(x2+9)] (2x)
g'(x) = x/√(x2+9)
g'(x0) = g'(-4) = -4/√(42+9)
g'(-4) = -4/5
By applying the values of g(x0) and g'(x0) in (1), we get
L(-4) = 5 + (-4/5)(x+4)
L(-4) = 5 - (4x/5) - (16/5)
L(-4) = (9/5) - (4x/5)
L(-4) = (1/5) (9-4x)
Problem 3 :
h(x) = x/(x+1) and x0 = 1
Solution :
Here f(x) and h(x) are equal.
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0)
h(x) = x/(x+1) and x0 = 1
h(x0) = 1/(1+1) = 1/2
h'(x) = [(x+1)(1)-x(1)] / (x+1)2
h'(x) = (x+1-x) / (x+1)2
h'(x) = 1/(x+1)2
h'(x0) = 1/(1+1)2
h'(x0) = 1/4
By applying the values of h(x0) and h'(x0) in (1)
L(1) = (1/2) + (1/4)(x-1)
L(1) = (1/2) + (x/4)-(1/4)
L(1) = (1/4)(1+x)
Problem 4 :
Since there were no problems on linear approximation on the second practice prelim, we are including some separately.
Consider the function f(x) = e2x.
(a) Determine the linearization L(x) of f(x) at the point (0, 1).
(b) Use your result in (a) to approximate e0.2.
Solution :
f(x) = e2x
f'(x) = e2x (2)
f'(x) = 2e2x
f'(0) = 2e2(0)
= 2(1)
= 2
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0)
When x = 0, f(0) = 1
L(0) = 1 + 2(x - 1)
= 1 + 2x - 1
= 2x
approximating e0.2:
L(0.2) = 2(0.2)
= 0.4
Problem 5 :
Find the linear approximation of f(x) = x sin (πx2) about x = 2. Use the approximation to estimate f(1.99)
Solution :
f(x) = x sin (πx2)
f'(x) = x(cos (πx2)(2x) + sin (πx2) (1)
f'(x) = 2x2cos (πx2) + sin (πx2)
At x = 2
f'(2) = 2(2)2cos (π(2)2) + sin (π(2)2)
= 8 cos (4π) + sin (4π)
= 8(1) + 0
= 8
f(x) = x sin (πx2)
f(2) = 2 sin (π(2)2)
= 2 (sin 4π)
= 2(0)
f(2) = 0
L(x) = f(x0) + f'(x0) (x-x0)
L(2) = f(2) + f'(2) (x - 2)
L(2) = 0 + 8 (x - 2)
L(2) = 8 x - 16
Approximating f(1.99) :