FINDING STANDARD DEVIATION OF UNGROUPED DATA
Example 1 :
Find the variance and standard deviation of the wages of 9 workers given below:
₹310, ₹290, ₹320, ₹280, ₹300, ₹290, ₹320, ₹310, ₹280.
Solution :
First, let us write the wages of 9 workers in ascending order.
280, 280, 290, 290, 300, 310, 310, 320, 320
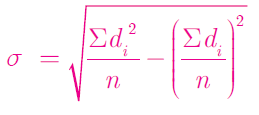
|
x 280 280 290 290 300 310 310 320 320 |
d = x - A d = x - 300 -20 -20 -10 -10 0 10 10 20 20 Σd = 0 |
d2 400 400 100 100 0 100 100 400 400 Σd2 = 2000 |
Σd2/n = 2000/9
(Σd/n)2 = (0/9)2 = 0
σ = √(2000/9)
σ = √222.22
σ = 14.91
Example 2 :
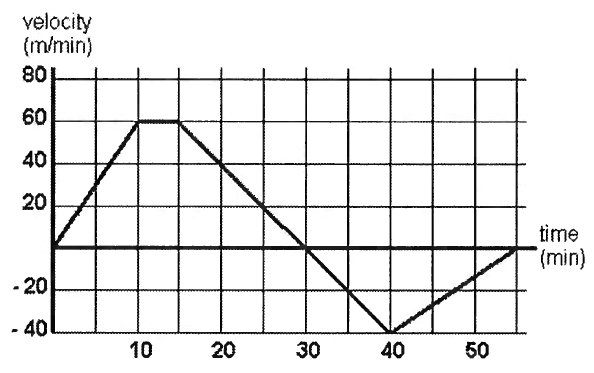
A wall clock strikes the bell once at 1 o’ clock, 2 times at 2 o’ clock, 3 times at 3 o’ clock and so on. How many times will it strike in a particular day. Find the standard deviation of the number of strikes the bell make a day.
Solution :
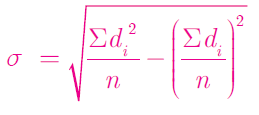
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 (From early morning to afternoon)
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 (From after noon to midnight)
Standard deviation for 1st n natural numbers
σ = [√((n2 - 1)/12)]
σ = [√((122 - 1)/12)]
σ = [√143/12]
σ = √11.92
σ = 3.45
Standard deviation for the given data = 3.45 + 3.45
σ = 6.9
Example 3 :
Find the standard deviation of first 21 natural numbers
Solution :
σ = [√((n2 - 1)/12)]
σ = [√((212 - 1)/12)]
σ = [√440/12]
σ = √36.67
σ = 6.05
Example 4 :
If the standard deviation of a data is 4.5 and if each value of the data is decreased by 5, then find the new standard deviation.
Solution :
The standard deviation will not change when we add or subtract some fixed constant to all the values.
So, the standard deviation for the new set of data is also 4.5.
Example 5 :
If the standard deviation of a data is 3.6 and each value of the data is divided by 3, then find the new variance and new standard deviation.
Solution :
While multiplying or dividing every element by the constant "k" then the standard deviation will be multiplied or divided by some constant "k".
Since we multiply every element by 3, we have to divide the standard deviation by 3 to obtain the standard deviation of new data set.
= 3.6/3
= 1.2
Variance = 1.44
Example 6 :
A greengrocer chain is to purchase oranges from two different wholesalers. They take five random samples of 40 oranges to examine them for skin blemishes. The counts for the number of blemished oranges are :
Wholesaler True fruit : 4 16 14 8 8
Wholesaler fresh fruit : 9 12 11 10 13
Find the mean and standard deviation for each data set, and hence compare the wholesale supplies.
Solution :
To find the standard deviation for this data set, we can use the formula
Wholesaler True fruit : 4 16 14 8 8
Mean = (4 + 16 + 14 + 8 + 8) / 5
= 50/5
= 10
|
x 4 16 14 8 8 |
(x - x̄) 4-10 = 6 16-10 = 6 14-10 = 4 8 - 10 = -2 8 - 10 = -2 |
(x - x̄)2 36 36 16 4 4 |
Σ(x - x̄)2 = 96
Wholesaler fresh fruit : 9 12 11 10 13
Mean = (9 + 12 + 11 + 10 + 13) / 5
= 55/5
= 11
|
x 9 12 11 10 13 |
(x - x̄) 9-11 = -2 12 - 11 = 1 11 - 11 = 0 10 - 11 = -1 13 - 11 = 2 |
(x - x̄)2 4 1 0 1 4 |
Σ(x - x̄)2 = 10
Clearly wholesaler Fresh fruit supplied oranges with more blemishes, on average but with less variability than for those supplied by True fruit.
Example 7 :
Basket ballers Andrew and Brad compare their goal throwing scores for last 8 matches.
Goals by Andrew :
23 17 31 25 25 19 28 32
Goals by Brad :
9 29 41 26 14 44 38 43
a) Find the mean and standard deviation for the number of goals thrown by each goal shooter for these matches.
b) Which measure is used to determine which of the goal shooters is more consistent ?
Solution :
To find the standard deviation for this data set, we can use the formula
Goals by Andrew :
23 17 31 25 25 19 28 32
Mean = (23 + 17 + 31 + 25 + 25 + 19 + 28 + 32) / 8
= 200/8
= 25
|
x 23 17 31 25 25 19 28 32 |
(x - x̄) 23 - 25 = 2 17 - 25 = 8 31 - 25 = 6 25 - 25 = 0 25 - 25 = 0 19 - 25 = -6 28 - 25 = 3 32 - 25 = 7 |
(x - x̄)2 4 64 36 0 0 36 9 49 |
Σ(x - x̄)2 = 198
Goals by Brad :
9 29 41 26 14 44 38 43
Mean = (9 + 29 + 41 + 36 + 14 + 44 + 38 + 43) / 8
= 244/8
= 30.5
|
x 9 29 41 26 14 44 38 43 |
(x - x̄) 9 - 30.5 = -21.5 29 - 30.5 = -1.5 41 - 30.5 = 10.5 26 - 30.5 = -4.5 14 - 30.5 = -16.5 44 - 30.5 = 13.5 38 - 30.5 = 7.5 43 - 30.5 = 12.5 |
(x - x̄)2 462.25 2.25 110.25 20.25 272.25 182.25 96.25 156.25 |
Σ(x - x̄)2 = 1302
a) For Andrew :
Mean = .25, standard deviation = 4.97
For Brad
Mean = .30.5, standard deviation = 12.56
b) Standard deviation is used to determine which of the goal shooters is more consistent.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 150)
Apr 25, 25 11:46 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 150) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19)
Apr 24, 25 11:10 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)
Apr 24, 25 11:06 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)