FINDING THE MEASURE OF THE REFERENCE ANGLE
The reference angle is the acute angle formed between the terminal arm and the x-axis. The reference angle is always positive and measures between 0° and 90°.
The reference angle always be lesser than 90 degree.
|
Angles in quadrants 2nd quadrant 3rd quadrant 4th quadrant |
Formula 180 - given angle given angle - 180 360 - given angle |
Example 1 :
What is the reference angle for each angle in standard position?
(a) 170° (b) 345° (c) 72° (d) 215°
Solution :
(a) 170°
Since the given angle lies in second quadrant, the reference angle of 170 is 180 - 170. That is 10°.
(b) 345°
Since the given angle lies in fourth quadrant, the reference angle of 345 is 360 - 345. That is 15°.
(c) 72°
Since the given angle lies in first quadrant, the reference angle is 72°.
(d) 215°
Since the given angle lies in third quadrant, the reference angle of 215 is 215 - 180. That is 35°.
Example 2 :
Determine the measure of the three other angles in standard position, 0° < θ < 360°, that have a reference angle of
(a) 45° (b) 60° (c) 30° (d) 75°
Solution :
Let θ be given angle.
The given angle lies in first quadrant. Reference angle
= 90 - 45
θR = 45
Angle in the second quadrat = 180 - θR
= 180 - 45
= 135°
Angle in third quadrant = 180 + θR
= 180 + 45
= 225°
Angle in fourth quadrant = 360 - θR
= 360 - 45
= 315°
So, the required angles are 135°, 225° and 315°.
(b) 60°
Solution :
Let θ be given angle.
The given angle lies in first quadrant. Reference angle
= 90 - 60
θR = 30
Angle in the second quadrat = 180 - θR
= 180 - 30
= 150°
Angle in third quadrant = 180 + θR
= 180 + 30
= 210°
Angle in fourth quadrant = 360 - θR
= 360 - 30
= 330°
So, the required angles are 150°, 210° and 330°.
(c) 30°
Solution :
Let θ be given angle.
Required angle in 2nd quadrant = 180 - θ
= 180 - 30 = 150
Required angle in 3rd quadrant = 180 + θ
= 180 + 30 = 210
Required angle in 4th quadrant = 360 - θ
= 360 - 30 = 330
Hence the required angles are 150, 210 and 330.
(d) 75°
Solution :
Let θ be given angle.
Required angle in 2nd quadrant = 180 - θ
= 180 - 75 = 105
Required angle in 3rd quadrant = 180 + θ
= 180 + 75 = 255
Required angle in 4th quadrant = 360 - θ
= 360 - 75 = 285
Hence the required angles are 105, 255 and 285.
Example 3 :
Sketch each angle in standard position, then identify the reference angle.
a) 460° b) -350° c) 695° d) -500°
Solution :
a) 460°
460 = 360 + 100
From this, we understand that the co-terminal angle lies in second quadrant.
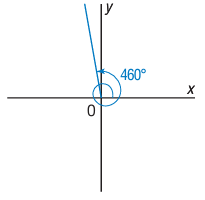
Co-terminal angle = 460° - 360°
= 100°
Reference angle lies in 2nd quadrant, then
= 180 - 100
= 80°
b) -350°
-350 = -270 - 80
Since the given angle is negative, we go for counterclockwise rotation. Co-terminal angle lies in first quadrant.
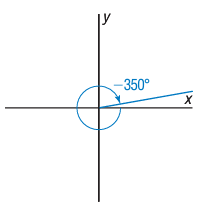
Co-terminal angle = 360° - 350°
= 10°
Reference angle is also 10°.
c) 695°
695 = -720 + 695
The angle lies in fourth quadrant. Co-terminal angle
= -25°
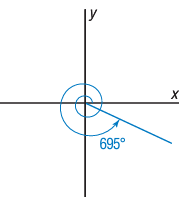
Reference angle = 25°
d) -500°
-500 = -360 - 140
= -140°
Since the given angle is negative, we go for counterclockwise rotation. Co-terminal angle lies in third quadrant.
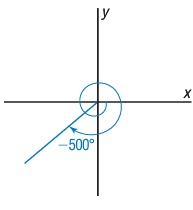
Reference angle = 140 - 270
Example 4 :
A windshield wiper has a length of 50 cm. The wiper rotates from its resting position at 30°, in standard position, to 150°. Determine the exact horizontal distance that the tip of the wiper travels in one swipe.
Solution :
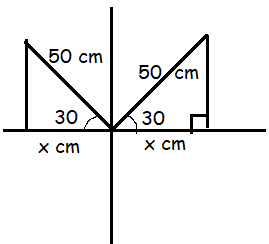
cos θ = adjacent side / hypotenuse
cos 30 = x/50
0.866 = x/50
x = 0.866(50)
x = 43.3
Required length = 2x
= 2(43.3)
= 86.6
So, the required horizontal distance is 86.6 cm.
Example 5 :
Find the values of the following trigonometric ratios :
i) sin 315 ii) cos 210 iii) cos (-480) iv) sin (-1125)
Solution :
i) sin 315
The given angle is in fourth quadrant. Since the given trigonometric ratio is sin, we use the negative sign.
Finding reference angle :
= 360 - 315
= 45
sin 315 = - sin 45
= 1/√2
ii) cos 210
The given angle is in third quadrant. Using ASTC, since the given trigonometric ratio is cos θ, we use the negative sign.
Finding reference angle :
= Given angle - 180
= 210 - 180
= 30
cos 210 = - cos 30
= -√3/2
iii) cos (-480)
cos (-480) = cos 480
480 = 360 + 120
The given angle is in second quadrant. Using ASTC, since the given trigonometric ratio is cos θ, we use the negative sign.
Finding reference angle :
= 180 - Given angle
= 180 - 120
= 60
cos 480 = -cos 60
= -1/2
iv) sin (-1125)
sin (-1125) = -sin 1125
= -sin (1080 + 45)
= -sin 45
The given angle is in first quadrant. Using ASTC, since the given trigonometric ratio is sin θ, we use the positive sign.
= - sin 45
= -1/√2
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 5)
Jan 06, 25 05:53 AM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 5) -
ALGEBRA - II : Simplifying Complex Fractions Problems and Solutions
Jan 06, 25 02:23 AM
ALGEBRA - II : Simplifying Complex Fractions Problems and Solutions -
ALGEBRA - II : Factoring Polynomials Problems with Solutions
Jan 06, 25 02:20 AM
ALGEBRA - II : Factoring Polynomials Problems with Solutions