HOW TO DETERMINE IF A FUNCTION IS MONOTONIC
Definition :
A function that is completely increasing or completely decreasing on the given interval is called monotonic on the given interval.
Usually, by looking at the graph of the function one can say whether the function is increasing or decreasing or neither.
The graph of an increasing function does not fall as we go from left to right while the graph of a decreasing function does not rise as we go from left to right.
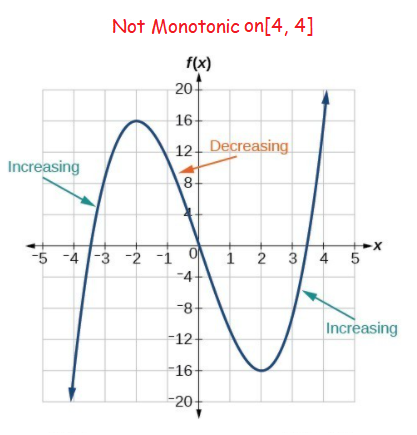
But if we are not given the graph, how do we decide whether a given function is monotonic or not ?
Test for monotonic functions :
Let I be an open interval. Let f : I → R be differentiable. Then
(i) The function f is increasing if and only if f ′(x) ≥ 0 for all x in I.
(ii) The function f is decreasing if and only if f ′(x) ≤ 0 for all x in I.
Note :
If a function changes its signs at different points of a region (interval) then the function is not monotonic in that region. So to prove the non- monotonicity of a function, it is enough to prove that f ′ has different signs at different points.
Example 1 :
Check whether the function
y = sin x + cos 2x
is monotonic on the interval [0, Π/4]
Solution :
f(x) = sin x + cos 2x
f'(x) = cos x - sin 2x [2 (1)]
f'(x) = cos x - 2 sin 2x
By applying x = 0, we get
f'(0) = cos 0 - 2 sin 2(0)
f'(0) = 1-2 (0)
f'(0) = 1 - 0
f'(0) = 1 > 0
By applying x = Π/4, we get
f'(Π/4) = cos Π/4 - 2 sin 2(Π/4)
f'(Π/4) = 1/√2 - 2 sin (Π/2)
f'(Π/4) = 1/√2 - 2 (1)
f'(Π/4) = 1/√2 - 2
f'(Π/4) = 0.707 - 2
f'(Π/4) = -1.292 < 0
Thus f′ is of different signs at 0 and π/4. So, the given function is not monotonic function on the interval [0, Π/4].
Example 2 :
Check whether the function
y = x sin x
is monotonic on the interval [Π/2, Π]
Solution :
f(x) = x sin x
f'(x) = x (cos x) + sin x (1)
f'(x) = x (cos x) + sin x
By applying x = Π/2
f'(0) = Π/2 (cos Π/2) + sin Π/2
f'(0) = Π/2 (0) + 1
f'(0) = 1 > 0
By applying x = Π
f'(Π) = Π (cos Π) + sin Π
f'(0) = Π (-1) + 0
f'(0) = - Π < 0
So, the function is not monotonic function.
Example 3 :
Discuss monotonicity of the function
(i) ex for all real numbers.
(ii) log x on (0, ∞)
Solution :
(i) f(x) = ex
Let f(x) = ex
f'(x) = ex
- If x > 0, then f′(x) > 0. The function is strictly increasing for all positive values of x.
- If x < 0 then f′(x) > 0. The function is strictly increasing for all negative values of x.
- If x = 0, then f'(x) = 1,we get positive value for f'(x).
So, the function monotonic on real numbers.
(ii) f(x) = log x on (0, ∞)
Let f(x) = log x
f'(x) = 1/x
If x > 0, then f′(x) > 0. The function is strictly increasing for all positive values of x.
So, the function monotonic on (0, ∞).
Example 4 :
Is the function sin (cos x) increasing or decreasing on the interval (Π, 3Π/2) ?
Solution :
Let f(x) = sin (cos x)
f'(x) = cos (cos x) . (– sin x)
On the interval (Π, 3Π/2), cos x lies in (–1, 0).
Hence, cos (cos x) > 0 (– sin x) > 0 on the interval (Π, 3Π/2).
Thus, we have f'(x) > 0 for all x in (Π, 3Π/2)
Hence, the function f(x) is strictly increasing for all x.
Example 5 :
Find the intervals where the following are increasing or decreasing.
i) f(x) = -x3 + 3x2 + 5
ii) f(x) = 3x4 - 8x3 + 2
Solution :
i) f(x) = -x3 + 3x2 + 5
f'(x) = -3x2 + 6x + 0
= -3x2 + 6x
f'(x) = -3x (x - 2)
The solutions are 0 and 2. By making it as intervals, we get
(-∞, 0) (0, 2) and (2, ∞)
|
Intervals |
f'(x) = -3x (x - 2) |
Increasing/ decreasing |
|
(-∞, 0) |
x = -1 f'(-1) = -3(-1) (-1-2) = 3(-3) = -9 |
Decreasing |
|
(0, 2) |
x = 1 f'(1) = -3(1) (1-2) = -3(-1) = 3 |
Increasing |
|
(2, ∞) |
x = 3 f'(3) = -3(3) (3-2) = -9(1) = -9 |
Decreasing |
ii) f(x) = 3x4 - 8x3 + 2
f'(x) = 12x3 - 24x2 + 0
= 12x3 - 24x2
f'(x) = 12x2 (x - 2)
The solutions are 0 and 2. By making it as intervals, we get
(-∞, 0) (0, 2) and (2, ∞)
|
Intervals |
f'(x) = 12x2 (x - 2) |
Increasing/ decreasing |
|
(-∞, 0) |
x = -1 f'(-1) = 12(-1)2(-1-2) = 12(-3) = -36 |
Decreasing |
|
(0, 2) |
x = 1 f'(1) = 12(1)2 (1 - 2) = 12(-1) = -12 |
Decreasing |
|
(2, ∞) |
x = 3 f'(3) = 12(3)2 (3 - 2) = 108(1) = 108 |
Increasing |
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 143)
Apr 13, 25 12:01 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 143) -
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions
Apr 12, 25 08:21 PM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 142)
Apr 11, 25 06:26 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 142)