HOW TO FIND APPROXIMATE VALUE USING BINOMIAL EXPANSION
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Example 1 :
Find 3√1001 approximately (two decimal places).
Solution :
3√1001 = (1001)1/3 = (1001)1/3
= (1000 + 1)1/3
= (1000)1/3 (1 + (1/1000))1/3
= 10 (1 + (1/1000))1/3
= 10 [1 + (1/3) (1/1000) + ...................]
= 10 [1 + (0.333)(0.001) ...................]
= 10 [1 + 0.000333 ...................]
= 10 [1.000333 ...................]
= 10.0033..........
Hence the approximate value of 3√1001 is 10.0033..........
Example 2 :
Prove that 3√(x3 + 6) − 3√(x3 + 3) is approximately equal to 1/x2 when x is sufficiently large.
Solution :
3√(x3 + 6) = (x3 + 6)1/3 = (x3)1/3 [1 + (6/x3)]1/3
= x [1 + (1/3)(6/x3) + ((1/3)(-2/3))/2 (6/x3)2 + ..............]
= x [1 + (2/x3) + (4/x6) + ..............]
= x + (2/x2) - (4/x5) + .............. ------(1)
3√(x3 + 3) = (x3 + 3)1/3 = (x3)1/3 [1 + (3/x3]1/3
= x [1 + (1/3)(3/x3) + ((1/3)(-2/3)/2)(3/x3)2 + ..............]
= x [1 + (1/x3) + (-1/x6) + ..............]
= x + (1/x2) - (1/x5) + .............. ------(2)
3√(x3 + 6) − 3√(x3 + 3)
= (x+(2/x2)-(4/x5)+ ..............)-(x+(1/x2)-(1/x5) + ..............)
= x - x + (2/x2) - (1/x2)
= 1/x2
Example 3 :
Prove that √(1−x)/(1+x) is approximately equal to 1 − x + x2 when x is very small.
Solution :
√(1−x)/(1+x) = [(1 - x)/(1 + x)]1/2
= [(1 - x)1/2/(1 + x)]1/2
= (1 - x)1/2(1 + x)-1/2
(1 - x)n
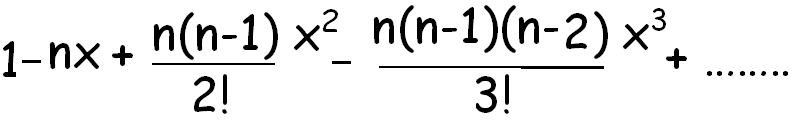
(1 - x)1/2 = 1 - (1/2)x + ((1/2)(-1/2)/2!)x2+....................
(1 + x)-1/2 = 1 - (x/2)x - (x2/8)+....................
(1 + x)-n
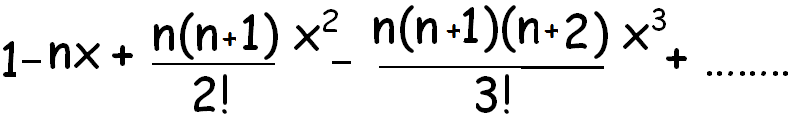
(1 + x)-1/2 = 1 - (1/2)x + ((1/2)(3/2)/2!)x2+....................
(1 + x)-1/2 = 1 - (x/2) + (3x2/8) +....................
(1 + x)-1/2 (1 + x)-1/2
= (1-(x/2)-(x2/8)+..........)(1 - (x/2)+(3x2/8) +..............)
= 1 - x/2 + 3x2/8 - x/2 + x2/4 - 3x3/16 - x2/8 + x3/16 + ..............
= 1 - [(x/2) + (x/2)] + [(3x2/8) + (x2/4)- (x2/8)
] + .........
= 1 - x + [(3x2+ 2x2-x2)/8]
= 1 - x + (4x2/8)
= 1 - x + x2/2
Hence proved.
Example 4 :
a) Find the first 4 terms of the binomial expansion, in ascending powers of x, of
(1 + x/4)8
giving each term in its simplest form.
(b) Use your expansion to estimate the value of (1.025)8, giving your answer to 4 decimal places.
Solution :
(x+a)n = nc0 x(n-0) a0 + nc1 x(n-1) a1 + nc2 x(n-2) a2 + ..........
x = 1, a = x/4 and n = 8
a)
Finding first 4 terms of the expansion :
= 8c0 1(8-0) (x/4)0 + 8c1 1(8-1) (x/4)1 + 8c2 1(8-2) (x/4)2 + 8c3 1(8-3) (x/4)3
= 18 (1) + 8 (17) (x/4) + 28 (16) (x2/16) + 56(15) (x3/64)
= 1 + 2x + (28/16) x2 + (56/64) x3
= 1 + 2x + (7/4) x2 + (7/8) x3
= 1 + 2x + (7x2/4) + (7x3/8)
b) (1.025)8 = (1 + 0.025))8
Here x/4 = 0.025
x = 0.025(4)
x = 0.1
= 1 + 2(0.1) + (7(0.1)2/4) + (7(0.1)3/8)
= 1 + 0.2 + 0.0175 + 0.000875
= 1.2184 (approximately)
Example 5 :
a) Find the first 4 terms of the binomial expansion, in ascending powers of x, of
(1 + x/2)10
giving each term in its simplest form.
(b) Use your expansion to estimate the value of (1.005)10, giving your answer to 5 decimal places.
Solution :
(x+a)n = nc0 x(n-0) a0 + nc1 x(n-1) a1 + nc2 x(n-2) a2 + ..........
x = 1, a = x/2 and n = 10
a)
Finding first 4 terms of the expansion :
= 10c0 1(10-0) (x/2)0 + 10c1 1(10-1) (x/2)1 + 10c2 1(10-2) (x/2)2 + 10c3 1(10-3) (x/2)3
= 110 (1) + 10 (19) (x/2) + (45/4) x2 + 120(17) (x3/8)
= 1 + 5x + (45/4) x2 + 15 x3
b) (1.005)10 = (1 + 0.005))10
Here x/2 = 0.005
x = 0.005(2)
x = 0.01
= 1 + 5(0.01) + (45/4) (0.01)2 + 15 (0.01)3
= 1 + 0.05 + 0.001125 + 0.000015
= 1.05114 (approximately)
Example 6 :
a) Find the first 4 terms of the binomial expansion, in ascending powers of x, of
(1 + ax)10
where a is a non zero constant. Give each term in its simplest form.
Given that in this expansion, the coefficient of x3 is double the coefficient of x2
b) Find the value of b.
Solution :
(x+a)n = nc0 x(n-0) a0 + nc1 x(n-1) a1 + nc2 x(n-2) a2 + ..........
(1 + ax)10
x = 1, a = ax and n = 10
a)
Finding first 4 terms of the expansion :
= 10c0 1(10-0) (ax)0 + 10c1 1(10-1) (ax)1 + 10c2 1(10-2) (ax)2 + 10c3 1(10-3) (ax)3
= 110 (1) + 10 (19) (ax) + 45 (18) (a2x2) + 120(15) (a3x3)
= 1 + 10 ax + 45a2x2 + 120 a3x3
b) Given that,
coefficient of x3 = double the coefficient of x2
120 a3 = 2(45a2)
120 a3 = 90 a2
a = 90/120
a = 3/4
So, the value of a is 3/4.
Example 7 :
a) Find the first 4 terms of the binomial expansion, in ascending powers of x, of
(2 + kx)7
where k is a non zero constant. Give each term in its simplest form.
Given that in this expansion, the coefficient of x2 is six times the coefficient of x
b) Find the value of k.
Solution :
(x+a)n = nc0 x(n-0) a0 + nc1 x(n-1) a1 + nc2 x(n-2) a2 + ..........
(1 + ax)10
x = 2, a = kx and n = 7
a)
Finding first 4 terms of the expansion :
= 7c0 2(7-0) (kx)0 + 7c1 2(7-1) (kx)1 + 7c2 2(7-2) (kx)2+7c3 2(7-3) (kx)3
= 27 (1) + 7 26 (kx) + 21 (25) (k2x2) + 35 24 (k3x3)
= 27 + 448 kx + 672 k2x2 + 560k3x3
b) Given that,
the coefficient of x2 = six times the coefficient of x
672 k2 = 6(448 k)
k = 6(448)/672
k = 4
So, the value of k is 4.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 43)
Jan 04, 26 01:38 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 43) -
90 Degree Clockwise Rotation
Jan 01, 26 06:58 AM
90 Degree Clockwise Rotation - Rule - Examples with step by step explanation -
US Common Core K-12 Curriculum Algebra Solving Systems of Equations
Jan 01, 26 04:51 AM
US Common Core K-12 Curriculum - Algebra : Solving Systems of Linear Equations
