HOW TO FIND LOCUS OF COMPLEX NUMBERS
Example 1 :
P represents the variable complex number z, find the locus of P if
Re (z + 1/z + i) = 1
Solution :
Let z = x + iy then
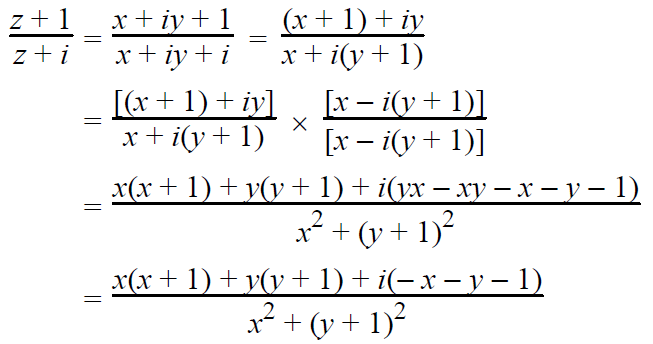
By equating the real part of te complex number to 1, we get
[x (x + 1) + y (y + 1)]/x2 + (y + 1)2 = 1
(x2 + x + y2 + y)/x2 + (y + 1)2 = 1
(x2 + y2 + x + y)/(x2 + (y2 + 2y + 1)) = 1
(x2 + y2 + x + y)/(x2 + y2 + 2y + 1) = 1
x2 + y2 + x + y = x2 + y2 + 2y + 1
x2 - x2 + y2 - y2 + x + y - 2y - 1 = 0
x - y - 1 = 0
So, the locus of the given complex number is
x - y - 1 = 0
Example 2 :
P represents the variable complex number z, find the locus of P if
|z - 5i| = |z + 5i|
Solution :
Let z = x + iy then
|z - 5i| = |z + 5i|
|(x + iy) - 5i| = |(x + iy) + 5i|
|x + i(y - 5)| = |x + i(y + 5)|
√x2 + (y - 5)2 = √x2 + (y + 5)2
Taking squares on both sides
x2 + (y - 5)2 = x2 + (y + 5)2
x2 + y2 - 10y + 25 = x2 + y2 + 10y+ 25
x2 + y2 - x2 - y2 - 10y - 10 y + 25 - 25 = 0
-20y = 0
y = 0
So, the locus of given complex number is
y = 0
Example 3 :
P represents the variable complex number z, find the locus of P if
| 2z − 3 | = 2
Solution :
Let z = x + iy then
| 2z − 3 | = 2
| 2(x + iy) − 3 | = 2
| 2x + i2y − 3 | = 2
| (2x − 3) + i 2y | = 2
√(2x − 3)2 + (2y)2 = 2
Taking squares on both sides
(2x)2 - 2(2x)(3) + 32 + (2y)2 = 22
4x2 - 12x + 9 + 4y2 = 4
4x2 + 4y2- 12x + 9 - 4 = 0
4x2 + 4y2- 12x + 5 = 0
So, the locus of given complex number is
4x2 + 4y2- 12x + 5 = 0
Example 4 :
On a sketch of argand diagram, show the locus representing complex numbers satisfying the equation :
|z| = |z - 4 - 3i|
Solution :
|z| = |z - 4 - 3i|
Let z = x + iy
|x + iy| = |x + iy - 4 - 3i|
|x + iy| = |(x - 4) + i(y - 3)|
On both side of the equal sign, since we have absolute sign, we find the modulus.
√x2 + y2 = √(x - 4)2 + (y - 3)2
x2 + y2 = (x - 4)2 + (y - 3)2
x2 + y2 = x2 - 2(x)(4) + 42 + y2 - 2y(3) + 32
x2 + y2 = x2 - 8x + 16 + y2 - 6y + 9
x2