HOW TO IDENTIFY THE TYPE OF FUNCTION IN SET THEORY
In this section, we will discuss the following types of functions with suitable examples.
(i) one – one (injection)
(ii) many – one
(iii) onto (Surjection)
(iv) one to one and onto (bijection)
(iv) into
(v) Constant function
(vi) Identity function
(vii) Real - valued function
One to One Function
A function f : A -> B is called one – one function if distinct elements of A have distinct images in B.
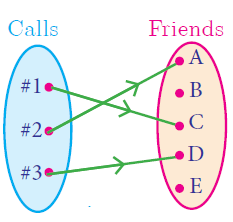
A one-one function is also called an injection.
Many to One Function
A function f : A -> B is called many-one function if two or more elements of A have same image in B.
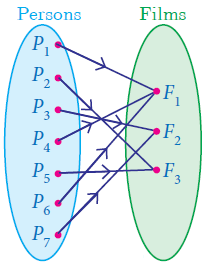
In other words, a function f : A-> B is called many-one if f it is not one–one.
Onto Function
A function f : A -> B is said to be onto function if the range of f is equal to the co-domain of f.
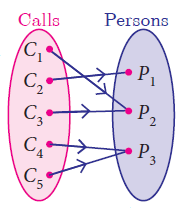
In other words, every element in the co-domain B has a pre-image in the domain A. An onto function is also called a surjection.
One to One and Onto Function
A function f : A -> B is called an into function if there exists atleast one element in B which is not the image of any element of A.
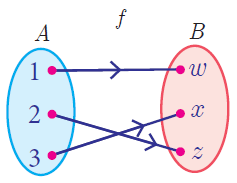
In other words, every element in the co-domain B has a pre-image in the domain A. An onto function is also called a surjection.
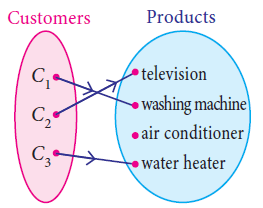
Into Function
Distinct elements of A have distinct images in B and every element in B has a pre-image in A.
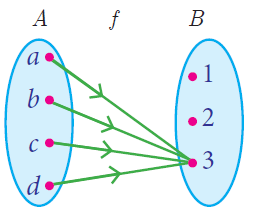
Constant Function
A function f : A -> B is called a constant function if the range of f contains only one element. That is, f (x ) = c , for all x ∊ A and for some fixed c ∊ B .
Identity Function
Let A be a non–empty set. Then the function f : A -> A defined by f (x) = x for all x ∊ A is called an identity function on A and is denoted by IA.
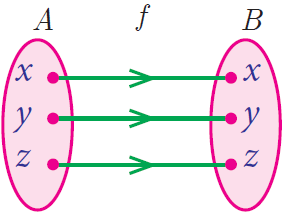
Real Valued Function
A function f : A -> B is called a real valued function if the range of f is a subset of the set of all real numbers ℝ . That is,f (A) ⊆ ℝ
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Pascal Triangle and Binomial Expansion
Feb 01, 25 10:12 AM
Pascal Triangle and Binomial Expansion - Concept - Examples -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Feb 01, 25 06:26 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 106)
Feb 01, 25 06:23 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 106)