IDENTIFY AND CLASSIFY POLYGONS
A polygon is any 2-dimensional closed shape formed by three or more line segments. Triangle is a polygon with least number sides, that is three.
If the shape had curves or didn't fully connect, then it can't be called a polygon.
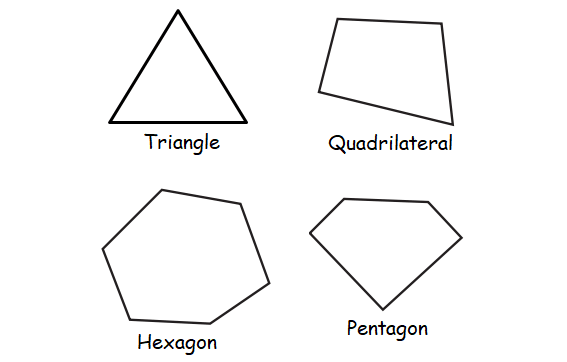
A polygon can be identified and classified by the number of sides they have.
|
Polygon Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Heptagon Octagon Nonagon Decagon n-gon |
Number of Sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 n |
Note :
A polygon with more than 10 sides will be named as n-gon.
Examples :
11-gon
12-gon
13-gon
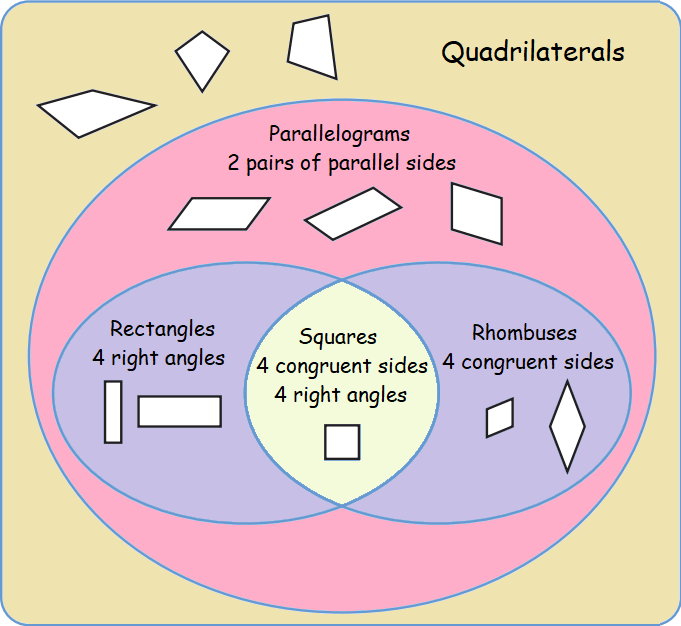
Quadrilaterals
A polygon formed by four line segments is called a quadrilateral.
The sum of all the four angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
Quadrilaterals with certain properties are given additional names. A trapezoid has exactly 1 pair of parallel sides. A parallelogram has 2 pairs
of parallel sides. A rectangle has 4 right angles. A rhombus has 4
congruent sides. A square has 4 congruent sides and 4 right angles.
Parallelogram
If the opposite sides of a quadrilateral are parallel, then it is a parallelogram.
In a parallelogram,
- Opposite sides are parallel and equal.
- Opposite angles are equal and sum of any two adjacent angles is 180°
- Diagonals bisect each other.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal.
Square
A square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles. It can also be defined as a rectangle in which two adjacent sides have equal length. A square with vertices ABCD would be denoted ABCD
Rhombus
A rhombus is a simple quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length.
- All sides are equal and opposite sides are parallel
- Opposite angles are equal and sum of any two adjacent angles is 180°.
- Diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
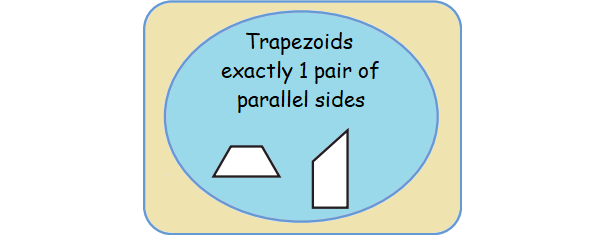
Trapezoid
Sides : One pair of opposite sides is parallel.
Angles : The angles at the ends of each non-parallel side are supplementary.
Diagonals : Diagonals need not be equal.
Isosceles Trapezoid
Sides : One pair of opposite sides is parallel, the other pair of sides is equal in length.
Angles : The angles at the ends of each parallel side are equal.
Diagonals : Diagonals are equal in length.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 150)
Apr 25, 25 11:46 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 150) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19)
Apr 24, 25 11:10 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 19) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)
Apr 24, 25 11:06 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 18)