IDENTIFYING OPPOSITES AND ABSOLUTE VALUE OF RATIONAL NUMBERS
Understand that positive and negative rational numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values.
Positive rational numbers are numbers greater than 0. Positive numbers can be written with or without a plus sign.
For example, 2/5 is the same as +2/5. Negative numbers are numbers less than 0.
Negative numbers must always be written with a negative sign.
For example, a rational number which is 2/3 less than 0 is '-2/3'.
Identifying Opposites of Rational Numbers
You can find the opposites of rational numbers that are not integers the same way we find the opposites of integers.
Two rational numbers are opposites, if they are the same distance from 0 but on different sides of 0.
It has been clearly illustrated in the picture given below.
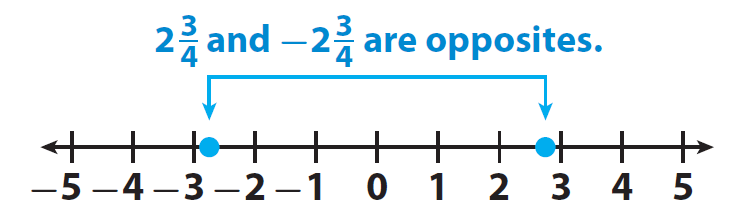
Question 1 :
Until May 15, 2007, the New York Stock Exchange priced the value of a share of stock in eighths, such as $27 1/8 or at $41 3/4 . The change in value of a share of stock from day to day was also represented in eighths as a positive or negative number.
The table shows the change in value of a stock over two days.

Graph the change in stock value for Wednesday and its opposite on a number line.
Answer :
Step 1 :
Graph the change in stock value for Wednesday on the number line.
The change in value for Wednesday is −4 1/4 . Graph a point 4 1/4 units below 0.
Step 2 :
Graph the opposite of -4 1/4
The opposite of -4 1/4 is the same distance from 0 but on the other side of 0.
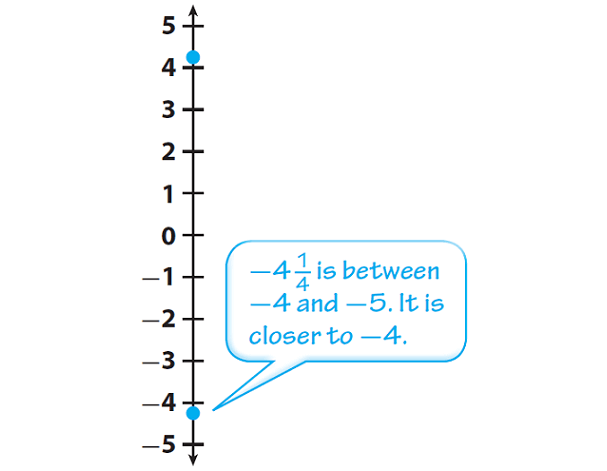
The opposite of -4 1/4 is 4 1/4.
The opposite of the change in stock value for Wednesday is 4 1/4.
Absolute Value of Rational Numbers
We can find the absolute value of a rational number that is not an integer the same way we find the absolute value of an integer.
The absolute value of a rational number is the number’s distance from 0 on the number line.
Question 2 :
The table shows the average low temperatures in January in one location during a five-year span. Find the absolute value of the average January low temperature in 2009.
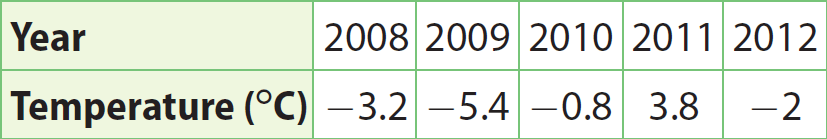
Answer :
Step 1 :
Graph the 2009 average January low temperature.
The 2009 average January low is -5.4 °C.
Graph a point 5.4 units below 0.
Step 2 :
Find the absolute value of -5.4.
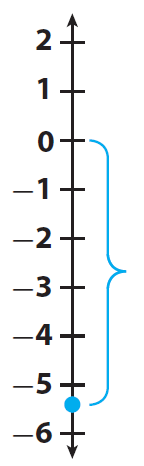
-5.4 is 5.4 units from 0.
Therefore,
|-5.4| = 5.4
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 134)
Apr 02, 25 12:40 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 134) -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Apr 02, 25 12:35 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part 135)
Apr 02, 25 12:32 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part 135)