INTEGRATION USING PARTIAL FRACTIONS EXAMPLES
Example 1 :
Integrate the following function with respect to x :
1/(x - 1) (x + 2)2
Solution :
Decompose the given rational function into partial fractions.
1/(x - 1) (x + 2)2 = A/(x - 1) + B/(x + 2) + C/(x + 2)2
1 = A(x+2)2 + B(x-1)(x+2) + C(x-1)
Plug x = 1
1 = 9A
A = 1/9
Plug x = -2
1 = C(-3)
C = -1/3
Plug x = 0
1 = 4A-2B-C
1 = 4(1/9) - 2B - (-1/3)
1 = (4/9)- 2B + (1/3)
1 - (4/9) - (1/3) = -2B
-2B = (9 - 4 - 3)/9
-2B = 2/9
B = -1/9
Integrate.
∫[1/(x - 1) (x + 2)2] dx
= (1/9)∫(1/(x-1))dx-(1/9)∫(1/(x+2)-(1/3)∫(1/(x+2)2 dx
= (1/9)log(x-1) - (1/9)log (x+2)-(1/3)(1/(x+2)) + c
= (1/9) [log(x - 1) - log(x + 2)] - (1/3)(1/(x+2)) + c
= (1/9) [log(x - 1)/(x - 2)] - (1/3(x + 2)) + c
Example 2 :
Integrate the following function with respect to x :
(3x - 9)/(x - 1)(x + 2)(x2 + 1)
Solution :
Decompose the given rational function into partial fractions.
(3x - 9)/(x - 1)(x + 2)(x2 + 1)
= A/(x - 1) + B/(x + 2) + (Cx + D)/(x2 + 1)
3x - 9 = A(x+2)(x2+1)+B(x-1)(x2+1)+(Cx+D)(x-1)(x+2)
Plug x = 1
3 - 9 = A(6)
-6 = 6A ==> A = -1
Plug x = -2
-6 - 9 = B(-3)(5)
-15 = -15B ==> B = 1
Plug x = 0
- 9 = 2A - B - 2D
-9 = 2(-1) - 1 - 2D
-9 + 3 = -2D
-6 = -2D
D = 3
3x - 9 = A(x+2)(x2+1)+B(x-1)(x2+1)+(Cx+D)(x-1)(x+2)
Plug x = -1
- 12 = A(1)(2) + B(-2)(2) + (-C+D)(-2)
-12 = 2A - 4B + 2C - 2D
-12 = 2(-1) - 4(1) + 2C - 2(3)
-12 = -2 - 4 - 6 + 2C
2C = -12 + 12
C = 0
Integrate.
∫[(3x - 9)/(x - 1)(x + 2)(x2 + 1)] dx
= -∫1/(x - 1) dx + ∫1/(x + 2) dx + ∫ 3/(x2 + 1) dx
= - log (x - 1) + log (x + 2) + 3 tan-1(x)
= log (x + 2)/(x - 1) + 3 tan-1(x) + c
Example 3 :
Integrate the following function with respect to x :
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2)
Solution :
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = x3/(x2 - 3x + 2)
In the given rational fraction, the highest exponent of x in numerator is greater than the highest exponent of x in denominator.
So, we can use long division to decompose the given rational function.
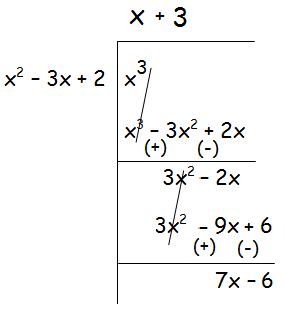
From the above long division, we have
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = (x + 3) + (7x - 6)/(x2 - 3x + 2)
x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = (x + 3) + (7x - 6)/(x - 1)(x - 2) ----(1)
Decompose (7x - 6)/(x - 1)(x - 2) into partial fractions.
(7x - 6)/(x - 1)(x - 2) = A/(x - 1) + B(x - 2)
Simplify.
7x - 6 = A(x - 2) + B(x - 1)
Plug x = 1
7(1) - 6 = A(1 -2 ) + B(1 - 1)
1 = A(-1)
A = -1
Plug x = 2
7(2) - 6 = A(2 -2 ) + B(2 - 1)
8 = B(1)
B = 8
Therefore we have
(1)-----> x3/(x - 1)(x - 2) = (x + 3) - 1/(x - 1) + 8/(x - 2)
Integrate.
∫[x3/(x - 1)(x - 2)] dx
= ∫(x + 3) dx -∫1/(x - 1) dx + 8∫1/(x - 2) dx
= x2/2 + 3x - log(x - 1) + 8log(x - 2) + C
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146)
Apr 18, 25 06:52 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146) -
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions
Apr 16, 25 09:25 PM
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)
Apr 16, 25 12:35 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)