INVESTIGATING SLOPE AND Y-INTERCEPT
The graph of every non vertical line crosses the y-axis. The y-intercept is the y-coordinate of the point where the graph intersects the y-axis. The x-coordinate of this point is always 0.
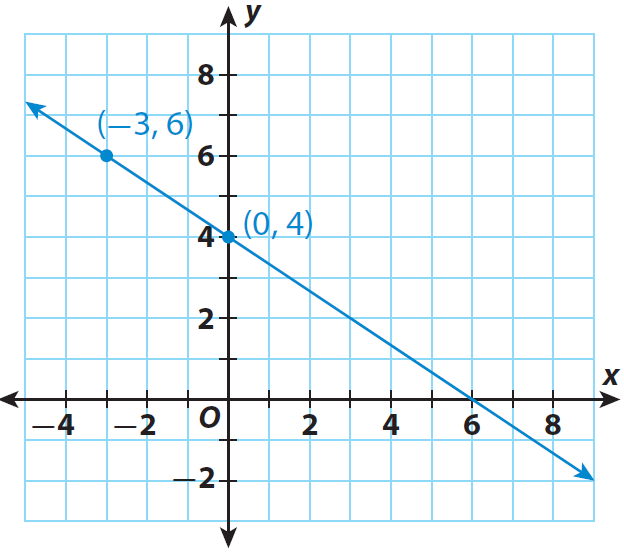
The graph given below represents the linear equation
y = (-2/3)x + 4
Step 1 :
Find the slope of the line using the points (0,4) and (-3,6).
m = change in y-values / change in x-values
m = (6 - 4) / (-3 - 0)
m = 2/(-3)
m = -2/3
Step 2 :
The line also contains the point (6, 0). What is the slope using (0, 4) and (6, 0)? Using (-3, 6) and (6, 0). What do you notice ?
m = change in y-values / change in x-values
m = (0 - 4) / (6 - 0)
m = -4/6
m = -2/3
It is the same as in Step 1.
Step 3 :
Find the value of y when x = 0 using the equation y = (-2/3)x + 4. Describe the point on the graph that corresponds to this solution.
4 ; (0, 4) is where the line intersects the y-axis.
Step 4 :
Compare your answer in Step 4 with the equation of the line.
The number 4 is the same as the number that is added to the x-term in the equation y = (-2/3)x + 4.
Step 5 :
After having discussed the above four steps, can we find the slope and y-intercept from the equation y = (-2/3)x + 4 without any calculation ?
Yes
The coefficient of x is slope and the number added to x-term is y-intercept.
That is,
Slope = -2/3
y-intercept = 4
Step 6 :
When can we find the slope and y-intercept of a line directly from the equation without any calculation ?
When the equation of a straight line is given in the form
y = mx + b,
we will be able to get slope and y-intercept of the line directly from the equation without any calculation.
That is,
slope = m
y-intercept = b
And also, the form y = mx + b is called slope intercept form equation of a straight line.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
ALGEBRA - II : Simplifying Complex Fractions Problems and Solutions
Jan 06, 25 02:23 AM
ALGEBRA - II : Simplifying Complex Fractions Problems and Solutions -
ALGEBRA - II : Factoring Polynomials Problems with Solutions
Jan 06, 25 02:20 AM
ALGEBRA - II : Factoring Polynomials Problems with Solutions -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Jan 04, 25 10:29 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)