MATH TERMS STARTING WITH D
Data :
In math data means combinations of items organized in rows and multiple variables organized in columns. Data are results of measurements and can be visualized using graphs and charts.
Decade :
Decade is a period of 10 years. For example, decade of the 20th century.
Decagon :
A polygon having 10 angles and 10 sides.
Decahedron :
In geometry, decahedron is a polyhedron with 10 faces.
Decimal :
Decimal is a real number system based on 10. Examples are Roman numerals, Brahmi, numerals, Hindu-Arabic numerals and Chinese numerals.
Denominator :
The lower part of the fraction is called denominator.
For example, in 3/4, 4 is the denominator.
Deductive proof and deductive reasoning :
In number theory, proof based on logical arguments that is justified by axioms or theorems. Deductive reasoning showing certain statements follow logically some stated assumptions.
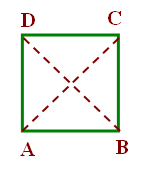
A line segment that connects two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon.AC and BD are diagonals of the square ABCD.
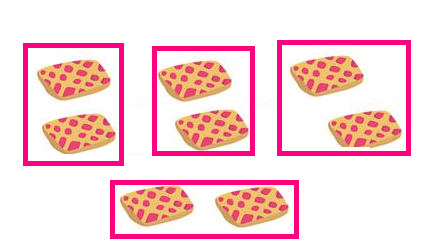
Division :
Division is nothing but splitting in to equal parts. Let us consider the following example.
Example :
There are 8 biscuits, and 4 friends want to share them, how do they divide the biscuits ?
Divisibility Test :
Divisibility Test is the topic in which we are going to see the shortcuts to predict one number is divisible by another number with out doing too much calculation.
Disjoint Sets :
Two or more sets are said to be disjoint if they have no common elements.Disjoint-sets are also known as non overlapping sets.
For example :
A = {2, 4, 6, 8} and B = {1, 3, 5, 7}. Here A and B have no common element. So A and B are disjoint sets.
Day Arithmetic :
Day Arithmetic is one of the important topic which is given some considerable weight age in SAT exam and other competitive exams.
If the divisor m = 7, then the arithmetic modulo 7 is called the day clock arithmetic. The remainders are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 correspond to week days Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and so on.
Different forms of numbers :
In mathematics we have different forms of numbers. The classification of numbers are natural number, whole number,Integer, fractions, decimals, percents, irrational and rational numbers, real numbers and complex numbers.
Distance Between Two Points :
Distance Between Two Points (x1, y1) and (x2 , y2)
√(x2 - x1)² + (y2 - y₁)²
Double angle formula :
sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A
sin 2A = 2 tan A/(1 + tan² A)
cos 2A = cos²A - Sin²A
cos 2A = 1 - 2sin²A
cos 2A = 2cos²A - 1
cos 2A = (1 - tan²A)/(1 + tan² A)
tan 2A = 2 tan A/(1 - tan² A)
sin²A = (1 - cos 2A)/2
cos²A = (1 + cos 2A)/2
Division of Polynomials :
Division of polynomials involves two cases, the first one is simplification,which is reducing the fraction and the second one is long division.
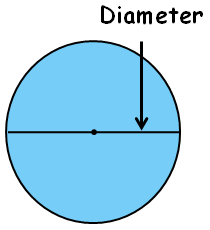
Diameter :
Diameter is the line which connect two ends of the circle and passing through the center.
De Moivre's theorem :
The process of mathematical induction can be used to prove a very important theorem in mathematics known as De Moivre's theorem.
If the complex number z = r(cos α + i sin α), then
Distance between parallel lines :
We can use the the following to find the distance between two parallel lines ax + by + c1 = 0 and ax + by + c2 = 0
|c1 - c2|/√(a2 + b2)
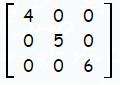
Diagonal matrix :
In a diagonal matrix all the entries along the diagonal are zero.
Direct variation :
When two quantities are said to be in direct variation if one quantity increases,then the other also increases or when one quantity decreases,the other also decreases.
Definite integrals :
A basic concept of integral calculus is limit. Generally the concept integration is used to find area between curves within certain limit.
Differentiation of Implicit Function :
When the relation between x and y is given by an equation in the form of f(x, y) = 0 and the equation is not easily solvable for y, then y is said to be implicit function.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 144)
Apr 14, 25 07:27 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 144) -
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 1)
Apr 14, 25 11:33 AM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 1) -
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 2)
Apr 14, 25 11:22 AM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 2)