MATH TERMS THAT START WITH R
Rate of Change :
If a quantity y depends on and varies with quantity x the rate of change of y with respect to x is dy/dx.
In other words we can define rate of change as the ratio of the rate of change in input values and rate of change in output values. Rate of change can be positive or negative.
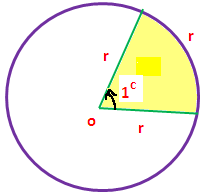
Radian :
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. It is the standard unit of angular measure. 1 radian results in same arc length and radius.
Radical :
n-th root of a quantity. A symbol used to indicate square of any number is called radical. The number which is under the root is called radical. √3 is called square root of 3.
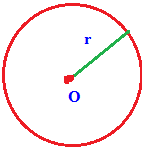
Radius :
A line from the center to the point on the circle.
Raise :
To multiply a number by itself a certain amount of time.
Example :
10 raise to the power 5 = 105
= 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 x 10
= 100000
Random :
Selecting an item from the given set of items without any order. That is like drawing a number from a hat.
The difference between the highest and lowest value.
Example :
Range of the given numbers
97, 46, 29, 37, 18
Range = 97-18
= 79
Rate :
Ratio that compares two different kinds of numbers or units.
Example :
miles per hour, dollars per pound.
Ratio :
Ratio that tells how one number is related to other number. Ratio of 'a' and 'b' is written as a/b or a : b.
Rational Number :
A number that can be expressed as a ratio of two numbers.
Rational Expression :
Rational expressions is a fraction of polynomial expressions. We can do all the operations like ordinary fractions with some considerations.
Rational Zero Theorem :
Rational zeros theorem gives the possible rational zeros of a polynomial function. Equivalently the theorem gives all the possible roots of an equation.
The theorem states that
If
f(x) = anxn+an-1xn-1+…. +a1x+a0
has integer coefficients and p/q(where p/q is reduced) is a rational zero, then .p is the factor of the constant term a0 and q is the factor of leading coefficient an.
Ray :
A line that has a starting point but no end point.

Real Number :
All the whole, rational and irrational numbers are called real numbers.
Reciprocal :
Multiplicative inverse of a number. One of two numbers whose product is 1.
Example:
Reciprocal of 2 is 1/2.
Ratio Formula :
Let A and B be two given points. Let P be a point on the line segment AB or AB produced. The P divides the line segment AB in to two segments AP and PB.
The lengths of AP and PB are AP and PB. These lengths are in some ratio m:n or that is AP:PB =m:n or AP/PB =m/n. If P lies inside AB, we say that P divides AB internally in the ratio m:n.
If P lies outside AB, that is P lies on AB produced, then we say P divides AB externally in the ratio m:n.
Relation :
In natural language relations are kind of relationship between two sets of information. In other words, Relation is a set of ordered pairs, usually defined by some sort of rule.
Representation of set :
Representation of set is being done usually in three forms:
- Set builder or Rule form
- Roster form or Tabular form
- Statement form or Descriptive form
Remainder Theorem :
If a polynomial f(x) of degree n, which is divided by (x-a), then the remainder is f(a), which is a constant and f(x) can be written as
f(x) = q(x)(x-a)+f(a)
where q(x) is the quotient polynomial with degree n-1.

Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Jan 02, 25 08:27 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 95)
Jan 02, 25 08:23 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 95) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 3)
Jan 01, 25 10:53 PM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 3)