OVERLAPPING ARCS
If two inscribed angles intercept the same arc, then the angles are congruent.
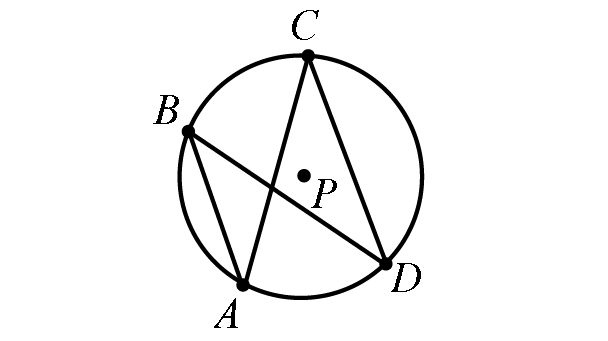
In the diagram above,
m∠ABD = m∠ACD
Example 1 :
Find m∠RST and m∠RUT.
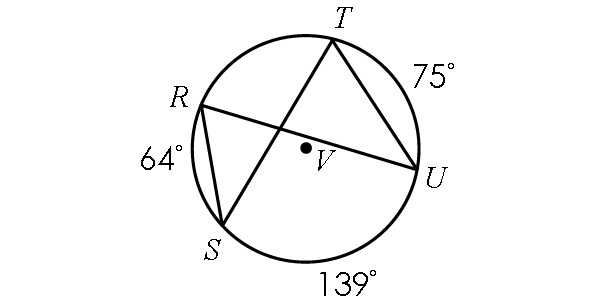
Solution :
In the diagram above,
m∠arc RT + m∠arc TU + m∠arc US + m∠arc SR = 360°
m∠arc RT + 75° + 139° + 64° = 360°
m∠arc RT + 75° + 139° + 64° = 360°
m∠arc RT + 278° = 360°
Subtract 278° from each side.
m∠arc RT = 82°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠RST = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc RT
m∠RST = 1/2 ⋅ 82°
m∠RST = 41°
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠RST and m∠RUT intercept the same arc RT. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠RUT = m∠RST
m∠RUT = 41°
Example 2 :
If m∠ABD = (6x + 26)° and m∠ACD = (13x - 9)°, find m∠arc AD.
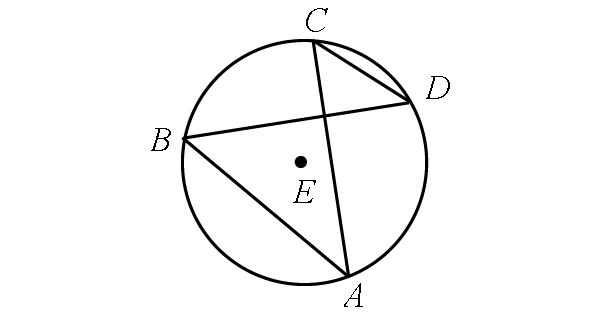
Solution :
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠ABD and m∠ACD intercept the same arc AD. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠ABD = m∠ACD
(6x + 26)° = (13x - 9)°
6x + 26 = 13x - 9
Subtract 6x from each side.
26 = 7x - 9
Add 9 to each side.
35 = 7x
Divide each side by 7.
5 = x
Finding m∠ABD.
m∠ABD = (6x + 26)°
Substitute x = 5.
m∠ABD = [6(5) + 26]°
m∠ABD = [30 + 26]°
m∠ABD = 56°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc AD = 2 ⋅ m∠ABD
m∠arc AD = 2 ⋅ 56°
m∠arc AD = 112°
Example 3 :
Find m∠GHJ and m∠GIJ.
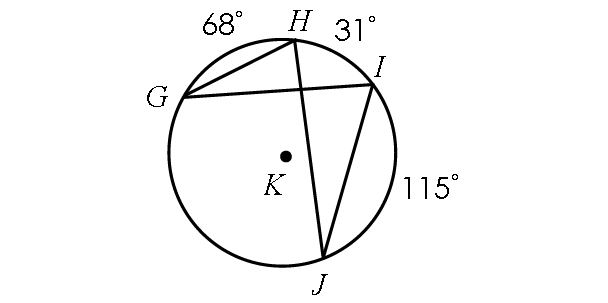
Solution :
In the diagram above,
m∠arc GJ + m∠arc JI + m∠arc IH + m∠arc HG = 360°
m∠arc GJ + 115° + 31° + 68° = 360°
m∠arc GJ + 214° = 360°
Subtract 214° from each side.
m∠arc GJ = 146°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠GHJ = 1/2 ⋅ m∠arc GJ
m∠GHJ = 1/2 ⋅ 146°
m∠GHJ = 73°
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠GHJ and m∠GIJ intercept the same arc GJ. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠GIJ = m∠GHJ
m∠GIJ = 73°
Example 4 :
If m∠LMP = (5x - 19)° and m∠LNP = (2x + 11)°, find m∠arc PL.
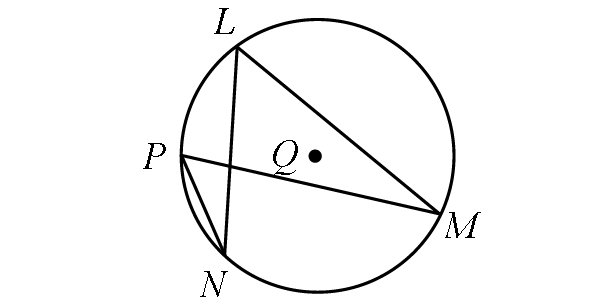
Solution :
In the diagram above, two inscribed angles m∠LMP and m∠LNP intercept the same arc LP. So, the angles are congruent.
m∠LMP = m∠LNP
(5x - 19)° = (2x + 11)°
5x - 19 = 2x + 11
Subtract 2x from each side.
3x - 19 = 11
Add 19 to each side.
3x = 30
Divide each side by 3.
x = 10
Finding m∠LMP.
m∠LMP = (5x - 19)°
Substitute x = 10.
m∠LMP = [5(10) - 19]°
m∠LMP = [50 - 19]°
m∠LMP = 31°
By Inscribed Angle Theorem,
m∠arc PL = 2 ⋅ m∠LMP
m∠arc PL = 2 ⋅ 31°
m∠arc PL = 62°
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
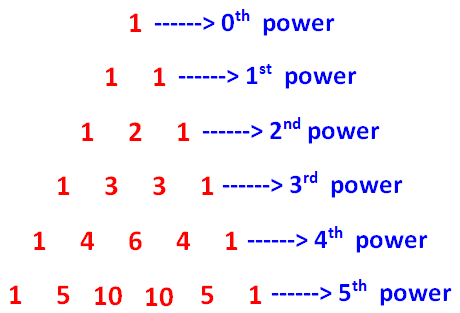
Pascal Triangle and Binomial Expansion
Feb 01, 25 10:12 AM
Pascal Triangle and Binomial Expansion - Concept - Examples -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Feb 01, 25 06:26 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 106)
Feb 01, 25 06:23 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 106)