PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON COORDINATE GEOMETRY FOR GRADE 10
Question 1 :
PQRS is a rectangle formed by joining the points P(-1,-1), Q(-1, 4), R(5, 4) and S(5,-1) . A, B, C and D are the mid-points of PQ, QR, RS and SP respectively. Is the quadrilateral ABCD a square, a rectangle or a rhombus? Justify your answer.
Solution :
Midpoint of the side PQ = A
Midpoint of the side QR = B
Midpoint of the side RS = C
Midpoint of the side SP = D
A = (x1 + x2)/2, (y1 + y2)/2
P(-1,-1), Q(-1, 4)
A = (-1 + (-1))/2, (-1 + 4)/2
A = (-1, 3/2)
Q(-1, 4) R(5, 4)
B = (-1 + 5)/2, (4 + 4)/2
B = (2, 4)
R(5, 4) and S(5,-1)
C = (5 + 5)/2, (4 + (-1))/2
C = (5, 3/2)
S(5,-1) and P(-1,-1)
D = (5 + (-1))/2, (-1 + (-1))/2
D = (2, -1)
Distance between AB = √(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2
|
A (-1, 3/2) B (2, 4) = √(2 + 1)2 + (4 - 3/2)2 = √9 + (25/4) = √61/2 |
B(3, 4) C (5, 3/2) = √(3-5)2 + (4-(3/2))2 = √4 + (25/4) = √61/2 |
|
C (5, 3/2) D (2, -1) = √(2-5)2 + (-1-(3/2))2 = √9 + (25/4) = √61/2 |
D (2, -1) A (-1, 3/2) = √(-1-2)2 + ((3/2)+1)2 = √9 + (25/4) = √61/2 |
Since the length of all sides are equal, it may be a square or rhombus not a rectangle.
I order to check if it is a square, let us find the slope of the sides AB and BC. If they are perpendicular, then it is square otherwise it is rhombus.
A (-1, 3/2) B (2, 4)
m1 = (y2 - y1)/(x2 - x1)
= (4 - (3/2))/(2 + 1)
= (5/2)/3
m1 = 5/6 ----(1)
B(3, 4) C (5, 3/2)
m2 = ((3/2) - 4)/(5 - 3)
= (-5/2)/2
m2 = -5/4 ----(2)
Since they are not perpendicular, it is not square. Hence it is rhombus.
Question 2 :
The area of a triangle is 5 sq.units. Two of its vertices are (2, 1) and (3, –2). The third vertex is (x, y) where y = x + 3 . Find the coordinates of the third vertex.
Solution :
Let the missing vertex be (x, y)
Area of triangle = 5
A (2, 1) B (3, -2) and C (x, y)
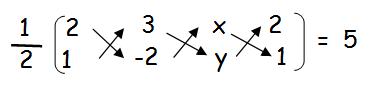
(1/2)[(-4 + 3y + x) - (3 - 2x + 2y)] = 5
x + 3y - 4 - 3 + 2x - 2y = 10
3x + y - 7 = 10
3x + y = 17 -----(1)
y = x + 3 (Given)
By applying the value of y in (1), we get
3x + x + 3 = 17
4x = 17 - 3
4x = 14
x = 7/2
By applying the value of x in the given equation, we get
y = (7/2) + 3
y = (7 + 6)/3
y = 13/3
Hence the third vertex is (7/2, 13/3)
Question 3 :
If the coordinates of points A and B are (–2, –2) and (2, –4) respectively, find the coordinates of the point P such that AP = (3/7) 𝐴𝐵, where P lies on the line segment AB.
Solution :
AP/AB = 3/7
AB = AP + PB
7 = 3 + PB
PB = 7 - 3
PB = 4
AP : PB = 3 : 4
To find the point which divides the line segment in the ratio m : n
A(–2, –2) and B(2, –4)
= [3(2) + 4(-2)]/(3 + 4), [3(-4) + 4(-2)]/(3 + 4)
= (6 - 8)/7, (-12 - 8)/7
= -2/7, -20/7
Question 4 :
If three consecutive vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A(1, -2 ), B(3, 6) and C (5, 10), find its fourth vertex D.
Solution :
In a parallelogram, midpoint of the diagonals will be equal.
Let the fourth vertex be D(x, y)
Midpoint of diagonal AC = Midpoint of diagonal BD
midpoint = (x1 + x2)/2, (y1 + y2)/2
Midpoint of AC = (1 + 5)/2, (-2 + 10)/2
= 6/2, 8/2
= (3, 4) ------(1)
Midpoint of BD = (3 + x)/2, (6 + y)/2 ------(2)
|
(3 + x)/2 = 3 3 + x = 6 x = 6 - 3 x = 3 |
(6 + y)/2 = 4 6 + y = 8 y = 8 - 6 y = 2 |
So, the fourth vertices is (3, 2).
Question 5 :
In what ratio is the line segment joining the points A (-2, -3) and B(3, 7) divided by the y-axis? Also, find the coordinates of the point of division
Solution :
When the point divides the y-axis, the value of x will be 0. The required point on the y-axis will be (0, y).
Let the required ratio be l : m
= (lx2 + mx1) / (l + m), (ly2 + my1) / (l + m)
l(3) + m(-2) / (l + m), l(7) + m(-3) / (l + m) = (0, y)
l(3) + m(-2) / (l + m) = 0
3l - 2m = 0
3l = 2m
l/m = 2/3
l : m = 2 : 3
Applying this ratio, we get
l(7) + m(-3) / (l + m) = (0, y)
[2(7) + 3(-3)] / (2 + 3) = y
14 - 9 / 5 = y
5/5 = y
y = 1
So, the required point on the y-axis is (0, 1).
Question 6 :
Points A (-1, y) and B(5, 7 ) lie on a circle with center O (2 , -3y ). Find the values of y. Hence, find the radius of the circle.
Solution :
Radius is the distance between center and point on the circle.
Distance between OC = distance between OB
√(x2 - x1)2 + (y2 - y1)2
√(2 + 1)2 + (-3y- y)2 = √(2 - 5)2 + (-3y - 7)2
√32 + (-4y)2 = √(-3)2 + (-3y - 7)2
(-4y)2 = (-3y - 7)2
16y2 = 9y2 + 42y + 49
16y2 - 9y2 - 42y - 49 = 0
7y2 - 42y - 49 = 0
y2 - 6y - 7 = 0
(y - 7)(y + 1) = 0
y = 7 and y = -1
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146)
Apr 18, 25 06:52 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146) -
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions
Apr 16, 25 09:25 PM
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)
Apr 16, 25 12:35 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)