PROBLEMS ON STANDARD INTEGRALS
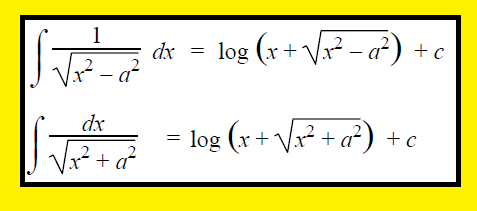
Problem 1 :
Evaluate
∫1/(1+9x2) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/(1+32x2) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
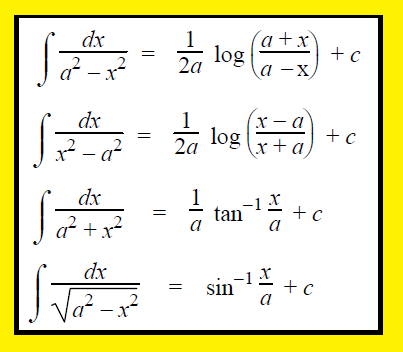
∫1/(a2+x2) dx = 1/a tan-1(x/a) + c
= 1/(1+(3x)2) dx
= 1/3 tan-1(3x/1) + C
= 1/3 tan-1(3x) + C
Problem 2 :
Evaluate
∫1/(1-9x2) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/(1-32x2) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/(a2-x2) dx = (1/2a) [log (a+x)/(a-x)] + c
a = 1 and x = 3x
= (1/2) [log(1+3x)/(1-3x)] + C
Problem 3 :
Evaluate
∫1/(1+x2/16) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/((1+(x/4)2) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/(a2+x2) dx = (1/a) tan-1 (x/a) + c
a = 1 and x = x/4
= 1 tan-1 ((x/4)/1) + C
= tan-1 (x/4) + C
Problem 4 :
Evaluate
∫1/((x+2)2-4) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/((x+2)2-22) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/(x2-a2) dx = (1/2a) [log (x-a)/(x+a)] + c
x = x+2 and a = 2
= (1/2⋅2) [log(x+2-2)/(x+2+2)] + C
= (1/4) [log(x/(x+4))] + C
Problem 5 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(25-x2) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(52-x2) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/√(a2-x2) dx = sin-1(x/a) + c
a = 5 and x = x
= sin-1(x/5) + c
Problem 6 :
Evaluate
1/√(4x2-25) dx
Solution :
= ∫ 1/√((2x)2-52) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/√(x2-a2) dx = log[x+√(x2-a2)]+C
a = 5 and x = 2x
= (1/2) log[2x+√(4x2-25)] + C
Problem 7 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(9x2+16) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√((3x)2+42) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/√(a2+x2) dx = log[x+√(a2+x2)] + c
x = 3x and a = 4
= log[3x+√(9x2+42) + C
= log[3x+√(9x2+16) + C
Problem 8 :
Evaluate
∫1/((3x+5)2+4) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/((3x+5)2+4) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/(x2+a2) dx = (1/a) tan-1(x/a) + c
x = 3x+5 and a = 2
= (1/2) [tan-1(3x+5)/2] + C
Problem 9 :
Evaluate
∫1/((x-2)2 + 1) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/((x-2)2 + 1) dx
The given exactly matches with the formula
∫1/(x2+a2) dx = (1/a) tan-1(x/a) + C
∫1/((x-2)2 + 1) dx = (1/1) tan-1[(x - 2) / 1] + C
= tan-1(x - 2) + C
Problem 10 :
Evaluate
∫x2/(x2 + 5) dx
Solution :
= ∫x2/(x2 + 5) dx
Adding and subtracting 5 in the numerator, we get
= ∫(x2 + 5 - 5)/(x2 + 5) dx
Decomposing into two fractions, we get
= ∫(x2 + 5)/(x2 + 5) dx - ∫(5/(x2 + 5)) dx
= ∫dx - 5∫(1/(x2 + 5)) dx
= x - 5 ∫(1/(x2 + √52 )) dx
= x - 5 [(1/√5) tan-1(x/√5)] + C
= x - [√5 tan-1(x/√5)] + C
Problem 11 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(1 + 4x2) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(1 + 4x2) dx
= ∫1/√(1 + (2x)2) dx
∫1/√(1 + x2) = log(x + √(1 + x2) + C
= log(2x + √(1 + 4x2)/2 + C
= (1/2) log (2x + √(1 + 4x2) + C
Problem 12 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(4x2 - 25) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(4x2 - 25) dx
= ∫1/√((2x)2 - 52) dx
∫1/√(1 - x2) = log(x + √(1 - x2) + C
= log(2x + √(4x2- 25))/2 + C
= (1/2) log(2x + √(4x2- 25)) + C
Problem 12 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(4x2 - 25) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(4x2 - 25) dx
= ∫1/√((2x)2 - 52) dx
∫1/√(1 - x2) = log(x + √(1 - x2) + C
= log(2x + √(4x2- 25))/2 + C
= (1/2) log(2x + √(4x2- 25)) + C
Evaluate
∫1/√(4x2 - 25) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(4x2 - 25) dx
= ∫1/√((2x)2 - 52) dx
∫1/√(1 - x2) = log(x + √(1 - x2) + C
= log(2x + √(4x2- 25))/2 + C
= (1/2) log(2x + √(4x2- 25)) + C
Problem 13 :
Evaluate
∫1/(x2 - 2x + 5) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/(x2 - 2x + 5) dx
Since we have quadratic at the denominator, we have to rewrite it as sum of difference of square using the method of completing the square.
x2 - 2x + 5 = x2 - 2⋅x⋅1 + 12 - 12 + 5
= (x - 1)2 - 1 + 5
= (x - 1)2 + 4
∫1/(x2 - 2x + 5) dx = ∫1 / [(x - 1)2 + 4] dx
∫1 / (x2 + a2) dx = (1/a) tan-1 (x/a) + C
= (1/2) tan-1 [(x-1)/2] + C
Problem 14 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(x2 + 12x + 11) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(x2 + 12x + 11) dx
Since we have quadratic at the denominator, we have to rewrite it as sum of difference of square using the method of completing the square.
x2 + 12x + 11 = x2 + 2⋅x⋅6 + 62 - 62 + 11
= (x + 6)2 - 36 + 11
= (x + 6)2 - 25
∫1/√[(x + 6)2 - 25] dx = ∫1/√[(x + 6)2 - 52] dx
∫1 / √(x2 - a2) dx = log (x + √(x2 - a2)) + C
= log ( (x + 6) + √[(x + 6)2 - 52] ) + C
Problem 15 :
Evaluate
∫1/√(12 + 4x - x2) dx
Solution :
= ∫1/√(12 + 4x - x2) dx
The quadratic that we have at the denominator is not in the standard form.
12 + 4x - x2 = -[x2 - 4x - 12]
= -[x2 - 2⋅x⋅2 + 22 - 22 - 12]
= -[(x - 2)2 - 4 - 12]
= -[(x - 2)2 - 16]
= 16 - (x - 2)2
= ∫1/√(12 + 4x - x2) dx = ∫1/√[16 - (x - 2)2] dx
= ∫1/√[42 - (x - 2)2] dx
∫1 / √(a2 - x2) dx = sin-1 (x/a) + C
∫1/√[42 - (x - 2)2] dx = sin-1 [(x-2)/4] + C
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 152)
Apr 28, 25 11:54 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 152) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 151)
Apr 26, 25 11:18 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 151) -
AP Calculus BC Problems with Solutions
Apr 26, 25 05:49 AM
AP Calculus BC Problems with Solutions