PROPERTIES OF ADDITION OF INTEGERS
In Math, The whole numbers and negative numbers together are called integers. The set of all integers is denoted by Z.
Z = {... - 2, - 1,0,1,2, ...}, is the set of all integers
Here, we are going to see the following four properties of addition of integers.
(i) Closure property
(ii) Commutative property
(iii) Associative property
(iv) Additive identity
Closure Property of Addition of Integers
Observe the following examples :
(i) 19 + 23 = 42
(ii) -10 + 4 = - 6
(iii) 18 + (- 47) = - 29
In general, for any two integers a and b, a + b is an integer.
Therefore the set of integers is closed under addition.
Commutative Property of Addition of Integers
Two integers can be added in any order. In other words, addition is commutative for integers.
We have 8 + (- 3) = 5 and (- 3) + 8 = 5
So, 8 + (- 3) = (- 3) + 8
In general, for any two integers a and b we can say,
a + b = b + a
Therefore addition of integers is commutative.
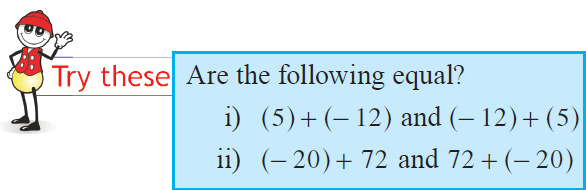
Associative Property of Addition of Integers
Observe the following example :
Consider the integers 5, – 4 and 7.
Look at
5 + [(– 4) + 7] = 5 + 3 = 8
and
[5 + (– 4)] + 7 = 1 + 7 = 8
Therefore, 5 + [(– 4) + 7] = [5 + (– 4)] + 7
In general, for any integers a, b and c, we can say,
a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c.
Therefore addition of integers is associative.

Additive Identity
When we add zero to any integer, we get the same integer.
Observe the example: 5 + 0 = 5.
In general, for any integer a, a + 0 = a.
Therefore, zero is the additive identity for integers.
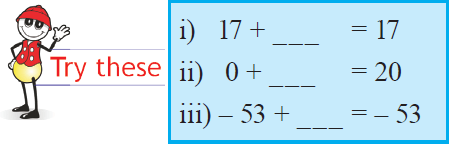
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 8)
Jan 30, 25 09:48 AM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 8) -
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Jan 29, 25 06:00 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 105)
Jan 29, 25 05:52 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 105)