PROVING TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES PRACTICE PROBLEMS
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
To learn the important trigonometric identities,
Abbreviations used in the problems :
* L.H.S -----> Left hand side
* R.H.S -----> Right hand side
Problem 1 :
Determine whether each of the following is an identity or not.
(i) cos2θ + sec2θ = 2 + sinθ
Solution :
L.H.S :
= cos2θ + sec2θ
= 1 - sin2θ + 1 + tan2θ
= 2 + tan2θ - sin2θ
≠ R.H.S
Since L.H.S and R.H.S are not equal, the given statement is not an identity.
(ii) cot2θ + cos θ = sin2θ
L.H.S :
= cot2θ + cosθ
= cosec2θ - 1 + cosθ ≠ R.H.S
Since L.H.S and R.H.S are not equal, the given statement is not an identity.
Problem 2 :
Prove the following identities
(i) sec2θ + cosec2θ = sec2θ cosec2θ
Solution :
L.H.S :
= sec2θ + cosec2θ
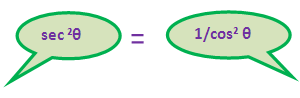
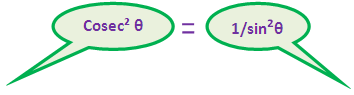
= (1/cos2θ)+ (1/sin2θ)
= (sin2θ + cos2θ)/(cos²θsin2θ)
= 1/(cos2θ ssin2θ)
= (1/cos2θ)(1/sin2θ)
= sec2θ cosec²θ
(ii) sinθ/(1 - cosθ) = cosecθ + cotθ
Solution :
L.H.S :
= sinθ/(1 - cosθ)
Multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of denominator.
= [sin θ(1 + cosθ)] x [(1 - cosθ)(1 + cosθ)]
Instead of (1 + cosθ)(1 + cosθ), we can write 1 - cos2θ by using the algebraic formula
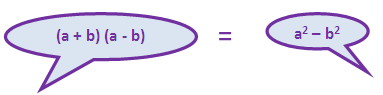
= [sinθ (1 + cosθ)]/(1 - cos2θ)
= [sinθ (1 + cosθ)]/sin2θ
= (1 + cosθ)]/sinθ
= (1/sinθ) + (cosθ/sinθ)
= cosecθ + cotθ
(iii) √(1 - sinθ)/(1 + sinθ) = secθ - tanθ
Solution :
L.H.S :
= √(1 - sinθ)/(1 + sinθ)
= √(1 - sinθ)/(1 + sinθ) x (1 - sinθ)/(1 - sinθ)
= √(1 - sinθ)2/[(1 + sinθ) x (1 - sinθ)]
= √(1 - sinθ)2/(12- sin2θ)
= √(1 - sinθ)2/(cos2θ)
= √[(1 - sinθ)/(cosθ)]2
= [(1 - sinθ)/(cosθ)]
= [(1/cosθ) - (sinθ/cosθ)]
= secθ - tanθ
= R.H.S
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 38)
Dec 29, 25 04:21 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 38) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39)
Dec 28, 25 11:20 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 39) -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 41)
Dec 28, 25 06:05 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 41)

