RATIONALIZATION OF SURDS EXAMPLES
When the denominator of an expression contains a term with a square root or a number under radical sign, the process of converting into an equivalent expression whose denominator is a rational number is called rationalizing the denominator.
If the product of two irrational numbers is rational, then each one is called the rationalizing factor of the other.
Rationalize the Denominator
Case 1 :
If the denominator is in the form of √a (where a is a rational number).
Then we have to multiply both the numerator and denominator by the same (√a).
Example 1 :
Rationalize the denominator 18/√6
Solution :
Step 1 :
We have to rationalize the denominator. Here we have √6 (in the form of √a). Then we have to multiply the numerator and denominator by √6
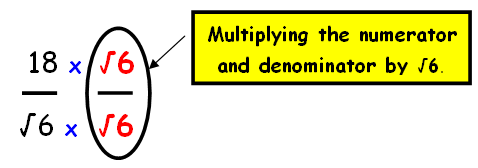
Step 2 :
By multiplying the numerators and denominators of first and second fraction , we get
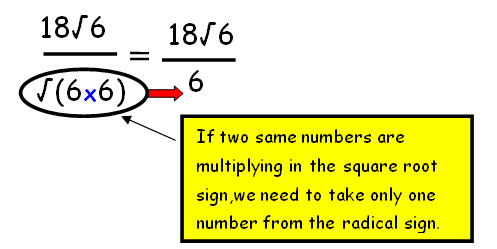
Step 3 :
By simplifications, we get 3√6
Case 2 :
If the denominator is in the form of a ± √b or a ± c √b (where b is a rational number).
Then we have to multiply both the numerator and denominator by its conjugate.
a + √b and a - √b are conjugate of each other.
a + c√b and a - c√b are conjugate of each other.
Example 2 :
Rationalize the denominator
4/(1+2√3)
Solution :
Step 1 :
Here we have (1 + 2√3) (in the form of a + c√b) in the denominator. Then we have to multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of (1 + 2√3).
Conjugate of (1 + 2√3) is (1 - 2√3)
= [4/(1 + 2√3)] ⋅ [(1 - 2√3) / (1 - 2√3)]
= [4(1 - 2√3)/(1 - 2√3)(1 - 2√3)]
= [4(1 - 2√3)/(1 - 2√3)(1 - 2√3)]
(a + b)(a - b) = a2 - b2
(1 - 2√3)(1 - 2√3) = 12 - (2√3)2
= [4(1 - 2√3)/(12 - (2√3)2)
= [4(1 - 2√3)/(1 - (4(3))
= [4(1 - 2√3)/(-11)
= (-4/11) + (2√3/11)
Example 3 :
Rationalize the denominator
(6 + √5)/(6-√5)
Solution :
Step 1 :
Here we have (6-√5) in the denominator. Then we have to multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of (6-√5).
Conjugate of (6-√5) is (6+√5)
= [(6 + √5)/(6-√5)] [(6 + √5)/(6 + √5)]
= (6 + √5)2 / (6-√5)(6 + √5)
(6 + √5)2 = 62 + 2(6)(√5) + (√5)2
= 36 + 12√5 + 5
= 41 + 12√5
Rationalizing the Denominator with Variables
Example 4 :
Rationalize the denominator
(2 + √3)/(2 - √3) = x + y√3
and find the value of x and y.
Solution :
(2 + √3)/(2 - √3)
Conjugate of the denominator 2 - √3 is 2 + √3.
= [ (2 + √3) / (2 - √3) ] [ (2 + √3) / (2 + √3) ]
= [ (2 + √3)2/ (2 - √3)(2 + √3) ]
(2 + √3)2
Expanding this using algebraic identity,
(a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
(2 + √3)2 = 22 + 2(2)√3 + √32
= 4 + 4√3 + 3
= 7 + 4√3