RATIONALIZING THE DENOMINATOR
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
When a radical contains an expression that is not a perfect root, for example, the square root of 3 or cube root of 5, it is called an irrational number.
So, in order to rationalize the denominator, we have to get rid of all radicals that are in denominator.
The following steps are involved in rationalizing the denominator of rational expression.
Step 1 :
Multiply both numerator and denominator by a radical that will get rid of the radical in the denominator.
If the radical in the denominator is a square root, then we have to multiply by a square root that will give us a perfect square under the radical when multiplied by the denominator.
Step 2 :
Make sure all radicals are simplified.
Some radicals will already be in a simplified form, but we have to make sure that we simplify the ones that are not.
Step 3 :
Simplify the fraction if needed.
Be careful. We cannot cancel out a factor that is on the outside of a radical with one that is on the inside of the radical. In order to cancel out common factors, they have to be both inside the same radical or be both outside the radical.
Rationalize the denominator :
Example 1 :
¹²⁄√₆
Solution :
= ¹²⁄√₆
Multiply both numerator and denominator by √6 to get rid of the radical in the denominator.
= ⁽¹²ˣ√⁶⁾⁄₍√₆ₓ√₆₎
= ⁽¹²ˣ√⁶⁾⁄₆
= 2√6
Example 2 :
4√5/√10
Solution :
Simplify.
4√5/√10 = 4√5/√(2 ⋅ 5)
= 4√5/(√2 ⋅ √5)
On the right side, cancel out √5 in numerator and denominator.
= 4/√2
On the right side, multiply both numerator and denominator by √2 to get rid of the radical in the denominator.
= (4 ⋅ √2)/(√2 ⋅ √2)
= 4√2/2
= 2√2
Example 3 :
5/√7
Solution :
Multiply both numerator and denominator by √7 to get rid of the radical in the denominator.
5/√7 = (5 ⋅ √7)/(√7 ⋅ √7)
= 5√7 / 7
Example 4 :
12/√72
Solution :
Decompose 72 into prime factor using synthetic division.
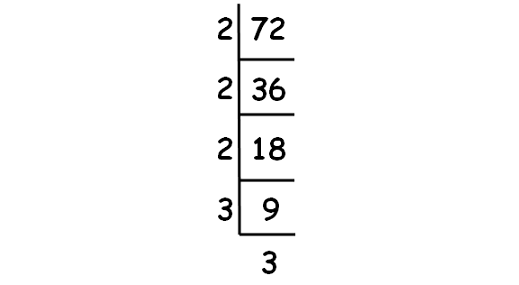
√72 = √(2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3)
= 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ √2
= 6√2
Then, we have
12/√72 = 12/6√2
Simplify.
= 2 / √2
On the right side, multiply both numerator and denominator by √2 to get rid of the radical in the denominator.
= (2 ⋅ √2) ⋅ (√2 ⋅ √2)
= 2√2/2
= √2
Example 5 :
1/(3 + √2)
Solution :
To get rid of the radical in denominator, multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of (3 + √2), that is by (3 - √2).
1/(3 + √2) = [1 ⋅ (3 - √2)]/[(3 + √2) ⋅ (3 - √2)]
= (3 - √2)/[(3 + √2) ⋅ (3 - √2)]
Using the algebraic identity a2 - b2 = (a + b)(a - b), simplify the denominator on the right side.
= (3 - √2)/[32 - (√2)2]
= (3 - √2)/(9 - 2)
= (3 - √2)/7
Example 6 :
(1 - √5)/(3 + √5)
Solution :
To get rid of the radical in denominator, multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of (3 + √5), that is by (3 - √5).
(1 - √5)/(3 + √5) = [(1 - √5) ⋅ (3 - √5)]/[(3 + √5) ⋅ (3 - √5)]
Simplify.
= [3 - √5 - 3√5 + 5]/[32 - (√5)2]
= (8 - 4√5)/(9 - 5)
= 4(2 - √5)/4
= 2 - √5
Example 7 :
(√x + y)/(x - √y)
Solution :
To get rid of the radical in denominator, multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of (x - √y), that is by (x + √y).
(√x + y)/(x - √y) = [(√x + y) ⋅ (x + √y)]/[(x - √y) ⋅ (x + √y)]
Simplify.
= [x√x + √xy + xy + y√y]/[(x2 - (√y)2]
= [x√x + √xy + xy + y√y]/(x2 - y2)
Example 8 :
3√(2/3a)
Solution :
3√(2/3a) = 3√2/3√3a
To rationalize the denominator in this case, multiply both numerator and denominator on the right side by the cube root of 9a2.
3√(2/3a) = [3√2 ⋅ 3√(9a2)]/[3√3a ⋅ 3√(9a2)]
Simplify.
= 3√(18a2)/3√(27a3)
= 3√(18a2)/3√(3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ a ⋅ a ⋅ a)
= 3√(18a2)/3a
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50)
Mar 06, 26 07:48 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 50) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49)
Mar 06, 26 06:47 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 49) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)
Mar 06, 26 05:24 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 48)


