SEGMENT AND ANGLE BISECTORS
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line between its endpoints.
An angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles. There are two types of angle bisectors. They are interior and exterior.
Bisecting a Segment
The midpoint of a segment is the point that divides, or the segment into two congruent segments. In this book, matching red congruence marks identify congruent segments in diagrams.
A segment bisector is a segment, ray, line, or plane that intersects a segment at its midpoint.
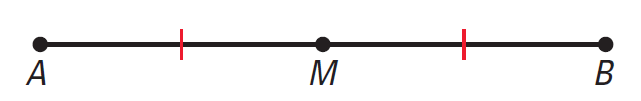
M is the mid point AB. Because M is on AB, we have
AM = MB
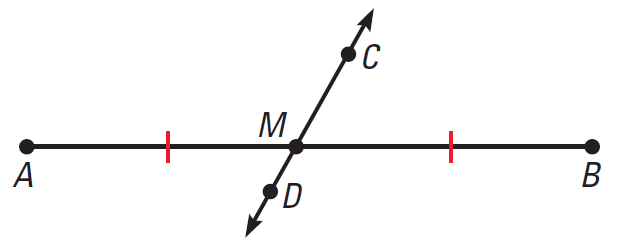
CD is a bisector of AB.
We can use a compass and a straightedge (a ruler without marks) to a segment bisector and midpoint of AB. A construction is a geometric drawing that uses a limited set of tools, usually a compass and a straightedge.
Construction Segment Bisector
Use the following steps to construct a bisector of AB and find the midpoint M of AB.
Step 1 :
Place the compass point at A. Use a compass setting greater than half the length of AB.
Draw an arc.
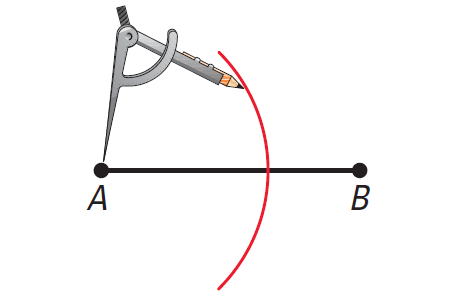
Step 2 :
Keep the same compass setting. Place the compass point at B. Draw an arc. It should intersect the other arc in two places.
Place the compass point at A. Use a compass setting greater than half the length of AB.
Draw an arc.
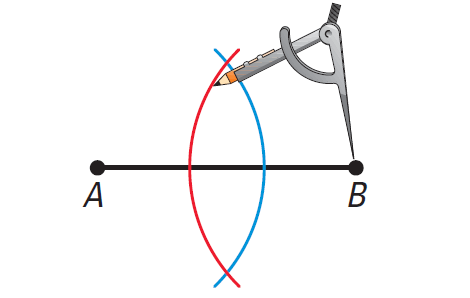
Step 3 :
Use a straightedge to draw a segment through the points of intersection. This segment bisects AB at M, the midpoint of AB. Keep the same compass setting. Place the compass point at B. Draw an arc. It should intersect the other arc in two places. Place the compass point at A. Use a compass setting greater than half the length of AB.
Draw an arc.
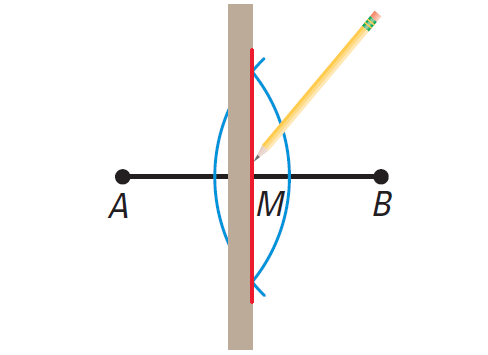
The Midpoint Formula
If we know the coordinates of the endpoints of a segment, we can calculate the coordinates of the midpoint. We simply take the mean, or average, of the x-coordinates and of the y-coordinates. This method is summarized as the Midpoint formula.
Let A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) be the two points in a coordinate plane as shown below.
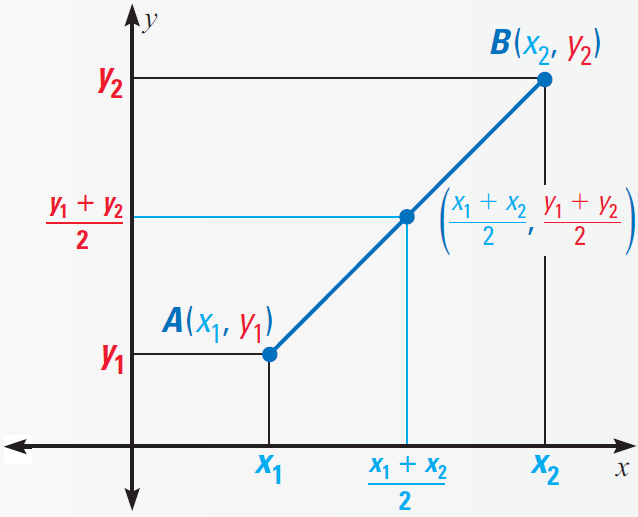
Then the midpoint of AB has coordinates
Bisecting an Angle
An angle bisector is a ray that divides an angle into two adjacent angles that are congruent.
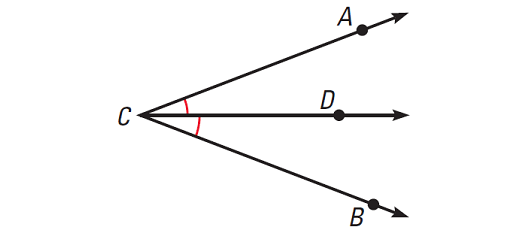
In the diagram given above, the ray CD bisects ∠ABC, because it divides the angle into two congruent angles, ∠ACD and ∠BCD.
Construction of Angle Bisector
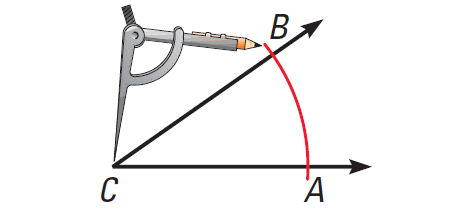
Use the following steps to construct an angle bisector of ∠C.
Step 1 :
Place the compass point at C. Draw an arc that intersects both sides of the angle. Label the intersections A and B.
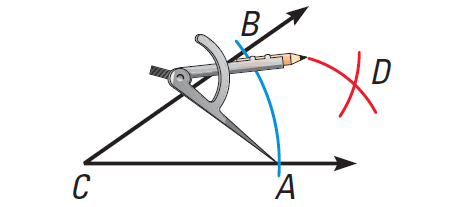
Step 2 :
Place the compass point at A. Draw an arc. Then place the compass point at B. Using the same compass setting, draw another arc.
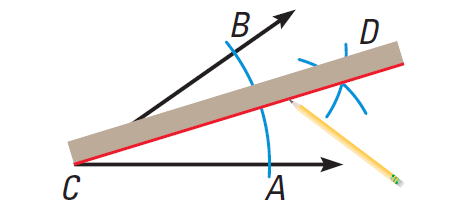
Step 3 :
Label the intersection D. Use a straightedge to draw a ray through C and D. This is the angle bisector. Place the compass point at A. Draw an arc. Then place the compass point at B. Using the same compass setting, draw another arc.
After we have constructed an angle bisector, we should check that it divides the original angle into two congruent angles. One way to do this is to use a protractor to check that the angles have the same measure.
Another way is to fold the piece of paper along the angle bisector. When we hold the paper up to a light, we should be able to see that the sides of the two angles line up, which implies that the angles are congruent.
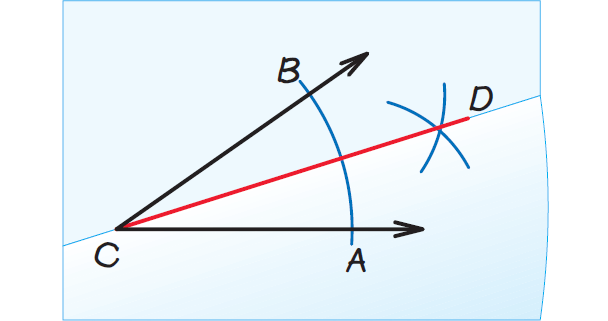
Fold on CD.
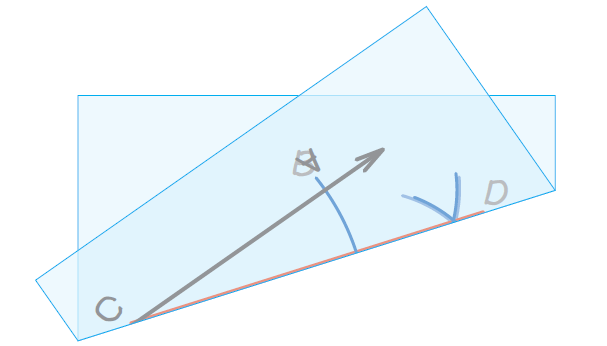
The sides of angles ∠BCD and ∠ACD line up.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146)
Apr 18, 25 06:52 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 146) -
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions
Apr 16, 25 09:25 PM
Logarithmic Derivative Problems and Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)
Apr 16, 25 12:35 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 145)