SIMPLIFYING RADICAL EXPRESSIONS USING CONJUGATES
Key Concept
Case 1 :
If the denominator is in the form of a ± √b or a ± c√b (where b is a rational number), then we have to multiply both the numerator and denominator by its conjugate.
a + √b and a - √b are conjugate to each other
a + c√b and a - c√b are conjugate to each other
Case 2 :
If the denominator is in the form of √a ± √b (where a and b are rational numbers), then we have to multiply both the numerator and denominator by its conjugate.
√a + √b and √a - √b are conjugate to each other
Radical Conjugate
If the product of two irrational numbers is rational, then the two irrational numbers are radical conjugate to the other.
Example :
The product of two irrational numbers √2 and √8 is the rational number 4.
That is,
√2 ⋅ √8 = √(2 ⋅ 8)
√2 ⋅ √8 = √16
√2 ⋅ √8 = √(4 ⋅ 4)
√2 ⋅ √8 = 4
So, √2 and √8 are radical conjugate to each other.
Solved Examples
Example 1 :
Simplify :
1 / (2 + √5)
Solution :
Simplifying the above radical expression is nothing but rationalizing the denominator.
So, rationalize the denominator.
Here, the denominator is 2 + √5.
In the given fraction, multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of 2 + √5. That is 2 - √5.
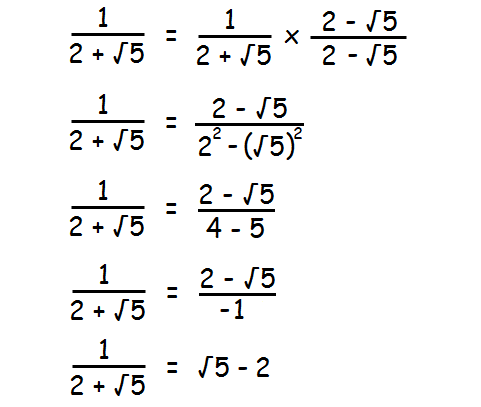
Example 2 :
Simplify :
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5)
Solution :
Simplifying the above radical expression is nothing but rationalizing the denominator.
So, rationalize the denominator.
Here, the denominator is 6 - √5.
In the given fraction, multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of 6 - √5. That is 6 + √5.
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5) = [(6+√5)(6+√5)] / [(6-√5)(6+√5)]
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5) = [(6+√5)(6+√5)] / [(6-√5)(6+√5)]
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5) = (6 + √5)2 / [62 - (√5)2]
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5) = [62 + 2(6)(√5) + (√5)2] / (36 - 5)
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5) = [36 + 12√5 + 5] / 31
(6 + √5) / (6 - √5) = (41 + 12√5) / 31
Example 3 :
Simplify :
1 / (8 - 2√5)
Solution :
Simplifying the above radical expression is nothing but rationalizing the denominator.
So, rationalize the denominator.
Here, the denominator is 8 - 2√5.
In the given fraction, multiply both numerator and denominator by the conjugate of 8 - 2√5. That is 8 + 2√5.
1 / (8 - 2√5) = 1(8+2√5) / [(8-2√5)(8+2√5)
1 / (8 - 2√5) = (8 + 2√5) / [82 - (2√5)2]
1 / (8 - 2√5) = (8 + 2√5) / [64 - (4 ⋅ 5]
1 / (8 - 2√5) = (8 + 2√5) / [64 - 20]
1 / (8 - 2√5) = (8 + 2√5) / 44
1 / (8 - 2√5) = 2(4 + √5) / 44
1 / (8 - 2√5) = (4 + √5) / 22
Example 4 :
Simplify :
2 / √3
Solution :
Simplifying the above radical expression is nothing but rationalizing the denominator.
So, rationalize the denominator.
Here, the denominator is √3.
In the given fraction, multiply both numerator and denominator by √3.
2 / √3 = (2√3) / (√3 ⋅ √3)
2 / √3 = 2√3 / 3
Example 5 :
Simplify :
1/√2 + 1/√5
Solution :
To add the above two fractions, make the denominators same.
Least common multiple of √2 and √5 is
= √2 ⋅ √5
= √(2 ⋅ 5)
= √10
Then,
1/√2 + 1/√5 = √5/√10 + √2/√10
1/√2 + 1/√5 = (√5 + √2) / √10
To rationalize the denominator on the right side, multiply both numerator and denominator by √10.
1/√2 + 1/√5 = [(√5+√2)√10] / (√10 ⋅ √10)
1/√2 + 1/√5 = (√50 + √20) / 10
1/√2 + 1/√5 = (√(5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 2) + √2 ⋅2 ⋅ 5) / 10
1/√2 + 1/√5 = (5√5 + 2√5) / 10
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions
Apr 12, 25 08:21 PM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 142)
Apr 11, 25 06:26 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 142) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 141)
Apr 11, 25 10:38 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 141)