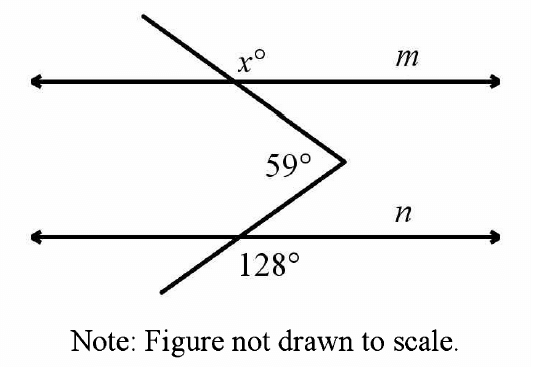
SYMBOLS USED IN SET THEORY
In set theory, we use different symbols to do operations like union, intersection etc., Here, we are going to see different symbols used in set theory to do the above mentioned operations.

Let us discuss the different symbols used in set theory in detail.
Union
Let X and Y be two sets.
Now, we can define the following new set.
X u Y = {z | z ∈ X or z ∈ Y}
(That is, z may be in X or in Y or in both X and Y)
X u Y is read as "X union Y"
Now that X u Y contains all the elements of X and all the elements of Y and the figure given below illustrates this.
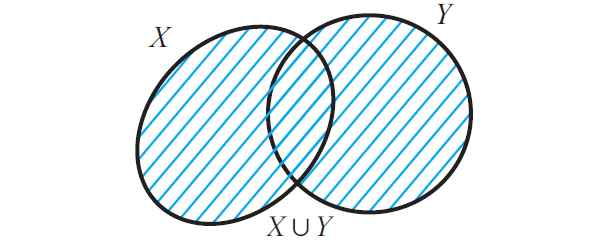
It is clear that X ⊆ X u Y and also Y ⊆ X u Y.
Intersection
Let X and Y be two sets.
Now, we can define the following new set.
X n Y = {z | z ∈ X and z ∈ Y}
(That is z must be in both X and Y)
X n Y is read as "X intersection Y"
Now that X n Y contains only those elements which belong to both X and Y and the figure given below illustrates this.
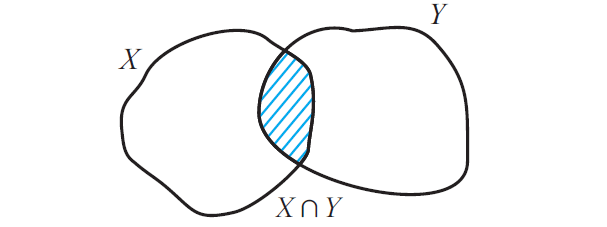
It is trivial that that X n Y ⊆ X and also X n Y ⊆ Y.
Set Difference
Let X and Y be two sets.
Now, we can define the following new set.
X\Y = {z | z ∈ X but z ∉ Y}
(That is z must be in X and must not be in Y)
X\Y is read as "X difference Y"
Now that X\Y contains only elements of X which are not in Y and the figure given below illustrates this.
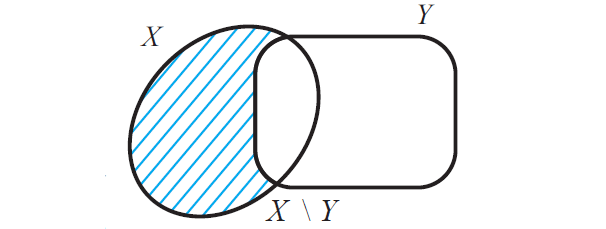
Some authors use A - B for A\B. We shall use the notation A\B which is widely used in mathematics for set difference.
Symmetric Difference
Let X and Y be two sets.
Now, we can define the following new set.
XΔY = (X\Y) u (Y\X)
X Δ Y is read as "X symmetric difference Y"
Now that X Δ Y contains all elements in X u Y which are not in X n Y and the figure given below illustrates this.
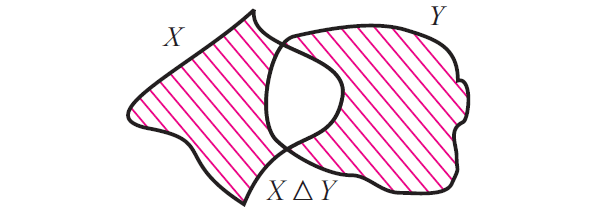
Complement
If X ⊆ U, where U is a universal set, then U\X is called the compliment of X with respect to U. If underlying universal set is fixed, then we denote U\X by X' and it is called compliment of X.
X' = U\X
The difference set set A\B can also be viewed as the compliment of B with respect to A.
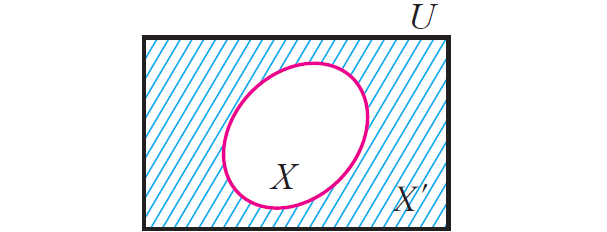
Disjoint Sets
Two sets X and Y are said to be disjoint if they do not have any common element. That is, X and Y are disjoint if
X n Y = ᵩ
It is clear that n(A u B) = n(A) + n(B), if A and B are disjoint finite set.
Subset of a Set
A set X is a subset of set Y if every element of X is also an element of Y.
In symbol we write
x ⊆ y
Reading Notation :

Read ⊆ as "X is a subset of Y" or "X is contained in Y".

Read ⊈ as "X is a not subset of Y" or "X is not contained in Y".
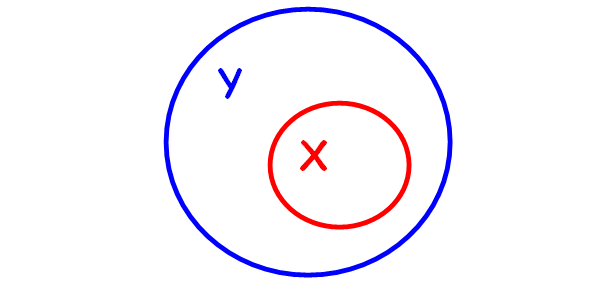
Proper Subset
A set X is said to be a proper subset of set Y if X ⊆ Y and X ≠ Y.
In symbol, we write X ⊂ Y.
Reading notation :

Read X ⊂ Y as "X is proper subset of Y".
The figure given below illustrates this.
Power Set
The set of all subsets of A is said to be the power set of the set A.
Reading notation :

The power set of A is denoted by P(A).
Super Set
A set X is said to be a proper subset of set Y if X ⊆ Y and X ≠ Y.
In symbol, we write X ⊂ Y.
Here,
Y is called super set of X
Formula to Find Number of Subsets
If A is the given set and it contains "n" number of elements, we can use the following formula to find the number of subsets.
Number of subsets = 2n
Formula to find the number of proper subsets :
Number of proper subsets = 2n-1
Cardinality of Power Set
We already know that the set of all subsets of A is said to be the power set of the set A and it is denoted by P(A).
If A contains "n" number of elements, then the formula for cardinality of power set of A is
n[P(A)] = 2n
Note :
Cardinality of power set of A and the number of subsets of A are same.
Null Set or Empty Set
A set which contains no element is called null set or empty set.
And it is denoted by { } or ∅.
Hence, the cardinal number of a null set is zero.
Null Set is a Subset or Proper Subset
Null set is a proper subset for any set which contains at least one element.
For example, let us consider the set A = {1}.
It has two subsets. They are { } and {1}.
Here null set is proper subset of A. Because null set is not equal to A.
If Null Set is a Super Set
If null set is a super set, then it has only one subset. That is { }.
More clearly, null set is the only subset to itself. But it is not a proper subset.
Because, { } = { }.
Therefore, A set which contains only one subset is called null set.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions
Apr 12, 25 08:21 PM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 142)
Apr 11, 25 06:26 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 142) -
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 141)
Apr 11, 25 10:38 AM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 141)