WRITING SAMPLE SPACE USING TREE DIAGRAMS EXAMPLES
Tree diagram allow us to see visually all possible outcomes of an random experiment. Each branch in a tree diagram represent a possible outcome.
(i) When we throw a die, then from the tree diagram the sample space can be written as
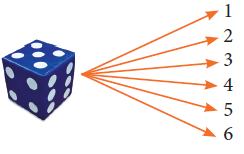
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }
When we toss two coins, then fr om the tree diagram the sample space can be written as
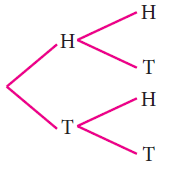
S = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
Example 1 :
Write the sample space for tossing three coins using tree diagram.
Solution :
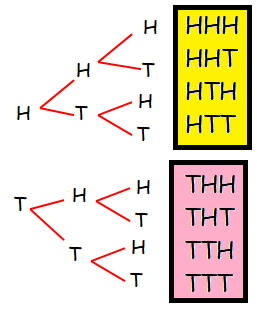
The required sample space
= {HHH. HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT}
Total number of outcomes = 8.
Example 2 :
Write the sample space for selecting two balls from a bag containing 6 balls numbered 1 to 6 (using tree diagram).
Solution :
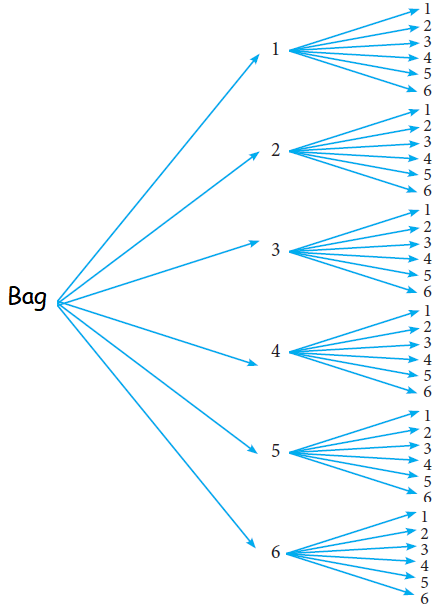
S = {(1, 1) (1, 2) (1, 3) (1, 4) (1, 5) (1, 6) (2, 1) (2, 2) (2, 3) (2, 4) (2, 5) (2, 6) (3, 1) (3, 2) (3, 3) (3, 4) (3, 5) (3, 6) (4, 1) (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 4) (4, 5) (4, 6) (5, 1) (5, 2) (5, 3) (5, 4) (5, 5) (5, 6) (6, 1) (6, 2) (6, 3) (6, 4) (6, 5) (6, 6)}
Total number of outcomes = 36
Example 3 :
If A is an event of a random experiment such that P(A) : P (A bar) = 17 : 15 and n(S) = 640 then find (i) P(A bar ) (ii) n(A).
Solution :
P(A) : P (A bar) = 17 : 15
P(A) / P (A bar) = 17 / 15
P(A) / [1 - P (A)] = 17 / 15
15 P(A) = 17 [1 - P(A)]
15 P(A) = 17 - 17 P(A)
15 P(A) + 17 P(A) = 17
32 P(A) = 17
P(A) = 17/32
P(A) = n(A) / n(S)
In order to make the denominator of p(A), let us multiply by 20
P(A) = (17/32) ⋅ (20/20)
P(A) = 340/640
P(A bar) = 1 - P(A)
= 1 - (340/640)
= 300/640
P(A bar) = 15/32
n(A) = 340
Example 4 :
A coin is tossed thrice. What is the probability of getting two consecutive tails?
Solution :

The required sample space
= {HHH. HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT}
n(S) = 8
Let "A" be the event of getting two consecutive tails
A = { HTT, TTH, TTT }
n(A) = 3
P(A) = n(A) / n(S)
P(A) = 3/8
Example 5 :
Illustrate, using a tree diagram, the possible outcomes when:
a) drawing two marbles from a bag containing many red, green, and yellow marbles.
Solution :
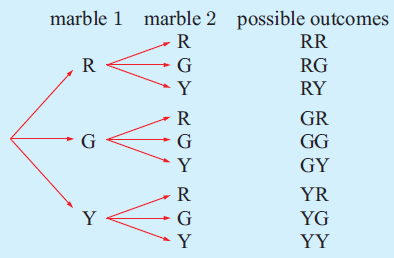
Example 5 :
List the sample space for the following :
a) twirling a square spinner labelled A, B, C, D
b) the sexes of a 2-child family
c) the order in which 4 blocks A, B, C and D can be lined up
d) the 8 different 3-child families.
Solution :
a) twirling a square spinner labelled A, B, C, D
Sample space = {A, B, C, D}
b) the sexes of a 2-child family
Let B be the boy child and G be girl child. Each family has 2 children. Then,
Sample space = {BB, GG, BG, GB}
{c) A, B, C and D can be lined up
Sample space = {ABCD, ABDC, ACBD, ACDB, ADBC, ADCB, BACD, BADC, BCAD, BCDA, BDAC, BDCA, CABD, CADB, CBAD, CBDA, CDAB, CDBA, DABC, DACB, DBAC, DBCA, DCAB, DCBA}
d) Let B be the boy child and G be girl child. Each family has 2 children. Then,
Sample space
= {GGG, GGB, GBG, BGG, GBB, BGB, BBG, BBB}
Example 6 :
Illustrate on a 2-dimensional grid the sample space for :
a) rolling a die and tossing a coin simultaneously
b) rolling two dice
c) rolling a die and spinning a spinner with sides A, B, C, D
d) twirling two square spinners, one labelled A, B, C, D and the other 1, 2, 3, 4.
Solution :
a) Possible outcomes when we toss a coin = {H, T}
Possible outcomes when we throw die = {1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
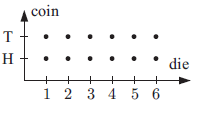
b) Possible outcomes when we throw die = {1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
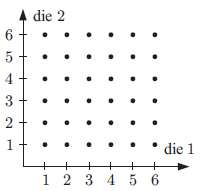
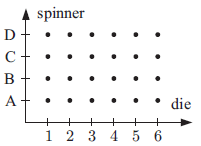
c) Possible outcomes when we throw die = {1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
When spinner is spinning with the face A, B, C and D, the
possible outcomes = {A, B, C, D}
d) Possible outcomes of spinner = {A, B, C, D}
Possible outcomes of spinner 2 = {1, 2, 3, 4}
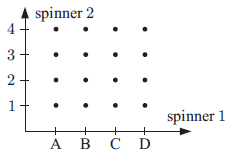
Example 7 :
Illustrate on a tree diagram the sample space for:
a) tossing a 5-cent and a 10-cent coin simultaneously
b) tossing a coin and twirling an equilateral triangular spinner labelled A, B, and C
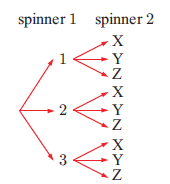
c) twirling two equilateral triangular spinners labelled 1, 2, and 3, and X, Y, and Z
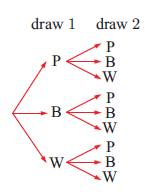
d) drawing two tickets from a hat containing a large number of pink, blue, and white tickets.
Solution :
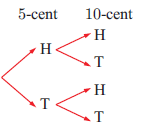
a) Possible outcomes when we toss coin = {H, T}
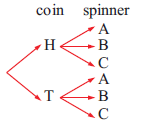
b) Possible outcomes for coin = {H, T}
Possible outcomes for spinner = {A, B, C}
c) Possible outcomes for spinners = {x, y, z} and {1, 2, 3}
d) Let P be pink ticket, B be blue ticket and W be white ticket
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 144)
Apr 14, 25 07:27 PM
Digital SAT Math Problems and Solutions (Part - 144) -
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 1)
Apr 14, 25 11:33 AM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 1) -
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 2)
Apr 14, 25 11:22 AM
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions (Part - 2)