FIND LCM WHEN POLYNOMIALS AND GCD ARE GIVEN
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Relationship between LCM and GCD :
f(x) ⋅ g(x) = LCM (f(x), g(x)) ⋅ GCD (f(x), g(x))
LCM(f(x), g(x)) = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD (f(x), g(x))
Find the LCM of each pair of the following polynomials
Example 1 :
x2 - 5x + 6, x2 + 4 x - 12 whose GCD is (x - 2)
Solution :
LCM ⋅ GCD = f(x) ⋅ g(x)
LCM = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD
f(x) = x2 - 5x + 6
g(x) = x2 + 4x - 12
GCD = (x-2)
x2 - 5x + 6 = (x - 2)(x - 3)
x2 + 4x - 12 = (x + 6)(x - 2)
LCM = (x - 2)(x - 3)(x + 6)(x - 2)/(x - 2)
By canceling common factors, we get
LCM = (x-2) (x-3) (x+6)
So, the required LCM is (x-2) (x-3) (x+6).
Example 2 :
x4 + 3x3 + 6x2 + 5x + 3, x4 + 2x2 + x + 2 whose GCD is x2 + x + 1
Solution :
x4 + 3x3 + 6x2 + 5x + 3, x4 + 2x2 + x + 2 whose GCD is x2 + x + 1
LCM = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD
f(x) = x4 + 3x3 + 6x2 + 5x + 3
g(x) = x4 + 2x2 + x + 2
GCD = x2 + x + 1
LCM = [(x4 + 3x3 + 6x2 + 5x + 3) (x4 + 2x2 + x + 2) ]/(x2 + x + 1)
To simplify this, we have to use long division.
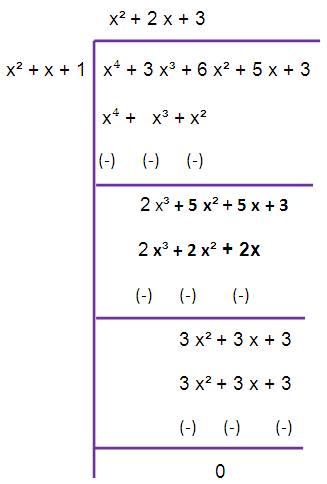
LCM = (x2 + 2x + 3) (x4 + 2x2 + x + 2)
So, the required LCM is (x2 + 2x + 3) (x4 + 2x2 + x + 2).
Example 3 :
2x3 + 15x2 + 2x - 35, x4 + 8x2 + 4x - 21 whose GCD is x + 7
Solution :
2x3 + 15x2 + 2x - 35, x4 + 8x2 + 4x - 21 whose GCD is x + 7
LCM = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD
f(x) = 2x3 + 15x2 + 2x - 35
g(x) = x4 + 8x2 + 4x - 21
GCD = x + 7
LCM = [(2x3 + 15x2 + 2x - 35) (x4 + 8x2 + 4x - 21)]/(x + 7)
To simplify this we have to use long division.
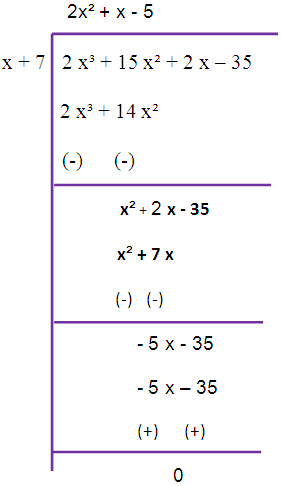
LCM = (2x2+x-5) (x4+8x2+4x-21)
So, the required LCM is (2x2+x-5) (x4+8x2+4x-21).
Example 4 :
2x3 - 3x2 - 9x + 5, 2x4 - x3 - 10x2 - 11x + 8 whose GCD is 2x - 1
Solution :
2x3 - 3x2 - 9x + 5, 2x4 - x3 - 10x2 - 11x + 8 whose GCD is 2x - 1
LCM = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD
f(x) = 2x3 - 3x2 - 9x + 5
g(x) = 2x4 -x3 - 10x2 - 11x + 8
GCD = 2x - 1
LCM = [(2x3 - 3x2 - 9x + 5) (2x4 - x3 - 10x2 - 11x + 8)]/(2x - 1)
To simplify this we have to use long division.
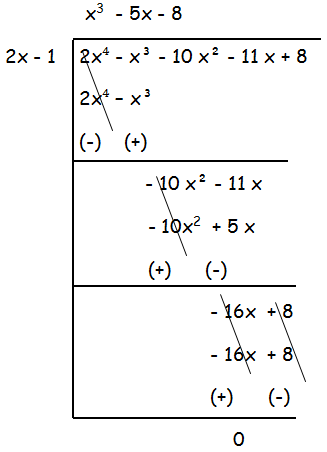
LCM = (x3 - 5x - 8) (2x3-3x2-9x+5)
So, the LCM is (x3 - 5x - 8) (2x3 - 3x2 - 9x + 5).
Example 5 :
If (x - a) is the GCD of x2 - x - 6 and x2 + 3x - 18, find the value of a.
a) 3 b) 6 c) 9 d) None of these
Solution :
Since (x - a) is GCD of the given polynomials
x2 - x - 6 and x2 + 3x - 18
We know that, by dividing each polynomial by x - a, we get 0 as remainder.
Let p(x) = x2 - x - 6
x - a = 0
x = a
a2 - a - 6 = 0
(a -3)(a + 2) = 0
a = 3 and a = -2
Accordingly the options given 3 is the value of a.
Example 6 :
Find the LCM of pair of polynomials given a2 + 4a - 12, a2 - 5a + 6 whose GCD is (a - 2)
Solution :
LCM ⋅ GCD = f(x) ⋅ g(x)
LCM = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD
f(x) = a2 + 4a - 12
g(x) = a2 - 5a + 6
GCD = (a - 2)
f(x) = a2 + 4a - 12 = (a + 6)(a - 2)
g(x) = a2 - 5a + 6 = (a - 2)(a - 3)
LCM = [f(x) ⋅ g(x)]/GCD
LCM = [ (a + 6)(a - 2) ⋅ (a - 2)(a - 3)]/ (a - 2)
By canceling common factors, we get
LCM = (a + 6) (a - 2) (a - 3)
So, the required LCM is (a + 6) (a - 2) (a - 3).
Example 7 :
Find the LCM of pair of polynomials given
x4 - 27a3 x, (x - 3a)2 whose GCD is (x - 3a)
Solution :
LCM ⋅ GCD = f(x) ⋅ g(x)
f(x) = x4 - 27a3 x
= x(x3 - 27a3)
= x(x3 - (3a)3)
f(x) = x(x - 3a)(x2 + 3ax + 9a2)
g(x) = (x - 3a)2
GCD = (x - 3a)
LCM = [x(x - 3a)(x2 + 3ax + 9a2) ⋅ (x - 3a)2]/(x - 3a)
= x (x2 + 3ax + 9a2) ⋅ (x - 3a)2
Example 8 :
(x -4) is the GCD of x2 - x - 12 and x2 - mx - 8, find the value of m
a) 4 b) 6 c) 2 d) none
Solution :
Let f(x) = x2 - x - 12
g(x) = x2 - mx - 8
Since x - 4 is a GCD of the given polynomials, they are divisible by this factor.
x - 4 = 0
x = 4
g(4) = 42 - m(4) - 8
0 = 16 - 4m - 8
0 = 8 - 4m
4m = 8
m = 8/4
m = 2
So, the value of m is 2.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
AP Calculus BC Problems with Solutions
Dec 20, 25 10:51 AM
AP Calculus BC Problems with Solutions -
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions (Part - 1)
Dec 20, 25 10:49 AM
AP Precalculus Problems and Solutions (Part - 1) -
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 1)
Dec 20, 25 10:49 AM
AP Calculus AB Problems with Solutions (Part - 1)
