FINDING THE MISSING LENGTH OF A RIGHT TRIANGLE
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
If the lengths of two sides of a right triangle are given, we can use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side.
Pythagorean Theorem :
Square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to sum of the squares of other two sides.
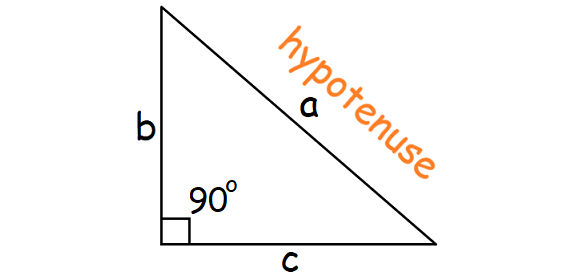
a2 = b2 + c2
If you know the values of any two variables, you can solve for the third variable using the above equation.
Note :
Hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle and it is always opposite to the right angle.
Example 1 :
In the right triangle shown below, find the value of 'a'.
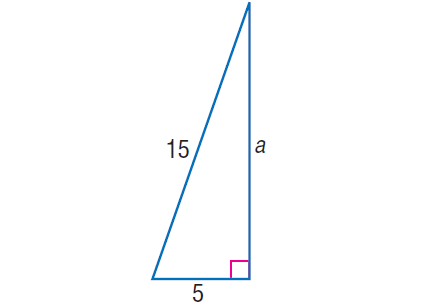
Solution :
In the right triangle above, by Pythagorean Theorem,
152 = 52 + a2
225 = 25 + a2
Subtract 25 from both sides.
200 = a2
Take square root on both sides.
√200 = √a2
√(2 x 10 x 10) = a
10√2 = a
Example 2 :
In the right triangle shown below, find the value of 'c'.
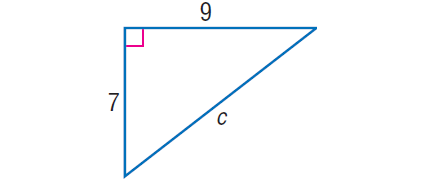
Solution :
In the right triangle above, by Pythagorean Theorem,
c2 = 72 + 92
c2 = 49 + 81
c2 = 130
Take square root on both sides.
√c2 = √130
c = √130
Example 3 :
In the right triangle shown below, find the value of 'c'.
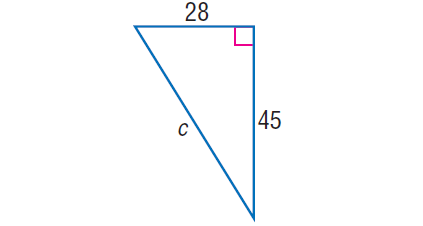
Solution :
In the right triangle above, by Pythagorean Theorem,
c2 = 282 + 452
c2 = 784 + 2025
c2 = 2809
Take square root on both sides.
√c = √2809
c = 53
Example 4 :
In the right triangle shown below, find the value of 'b'.
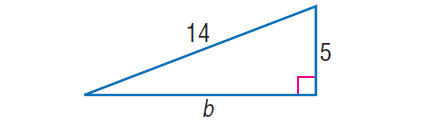
Solution :
In the right triangle above, by Pythagorean Theorem,
142 = 52 + b2
196 = 25 + b2
Subtract 25 from both sides.
171 = b2
√171 = √b2
√171 = b
Example 5 :
In the right triangle shown below, find the value of 'a'.
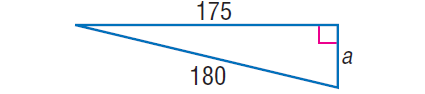
Solution :
In the right triangle above, by Pythagorean Theorem,
1802 = a2 + 1752
32400 = a2 + 30625
Subtract 30625 from both sides.
1775 = a2
√1775 = √a2
√(5 x 5 x 71) = a
5√71 = a
Example 6 :
In the right triangle shown below, find the value of 'b'.
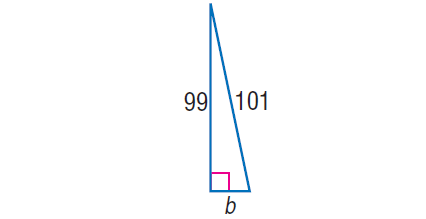
Solution :
In the right triangle above, by Pythagorean Theorem,
1012 = b2 + 992
10201 = b2 + 9801
Subtract 9801 from both sides.
400 = b2
√400 = √b2
20 = b
Example 7 :
Let a, b and c be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. If a = 16, b = 63 and c is the length of hypotenuse, then find the value of c.
Solution :
By Pythagorean Theorem,
c2 = a2 + b2
Substitute a = 16 and b = 63.
c2 = 162 + 632
c2 = 256 + 3969
c2 = 4225
Take square root on both sides.
√c2 = √4225
c = 65
Example 8 :
Let a, b and c be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. If a = 16, c = 34 and c is the length of hypotenuse, then find the value of b.
Solution :
By Pythagorean Theorem,
c2 = a2 + b2
Substitute a = 16 and c = 34.
342 = 162 + b2
1156 = 256 + b2
Subtract 256 from both sides.
900 = b2
Take square root on both sides.
√900 = √b2
30 = b
Example 9 :
Let a, b and c be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. If b = √112, c = 3 and a is the length of hypotenuse, then find the value of a.
Solution :
By Pythagorean Theorem,
a2 = b2 + c2
Substitute b = √112 and c = 3.
a2 = (√112)2 + 32
a2 = 112 + 9
a2 = 121
Take square root on both sides.
√a2 = √121
a = 11
Example 10 :
Let a, b and c be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. If a = 7y, c = 3y and a is the length of hypotenuse, then find the value of b in terms of y.
Solution :
a2 = b2 + c2
(7y)2 = b2 + (3y)2
49y2 = b2 + 9y2
Subtract 9y2 from both sides.
40y2 = a2
Take square root on both sides.
√(40y2) = √a2
2y√10 = a
Example 11 :
The bottom of a ladder must be placed 3 feet from a wall. The ladder is 12 feet long. How far above the ground does the ladder touch the wall?
Solution :
Let x be the distance from ground to tip of the wall it touches.
Using Pythagorean theorem,
122 = 32 + x2
144 = 9 + x2
x2 = 144 - 9
x2 = 135
x = √135
x = √(5 x 3 x 3 x 3)
= 3√15 ft
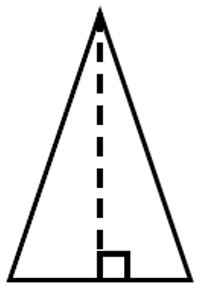
Example 12 :
An isosceles triangle has congruent sides of 20 cm. The base is 10 cm. What is the area of the triangle?
Solution :
Half of the base = 5 cm, side length = 20 cm
Let x be the height of the triangle.
202 = 52 + x2
400 = 25 + x2
x2 = 400 - 25
x2 = 375
x = √375
x = √(5 x 5 x 5 x 3)
= 5√15 cm
Example 13 :
The area of a square is 81 cm2. Find the length of diagonal.
Solution :
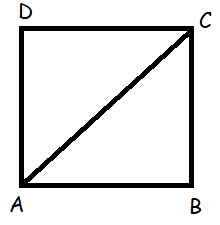
Let x be the side length of square.
Area of square = 81
a2 = 81
a2 = 92
a = 9
Let d be the length of diagonal. Then,
d2 = a2 + a2
d2 = 92 + 92
= 81 + 81
= 162
d = √162
d = √(2 x 9 x 9)
d = 9√2
So, the length of the diagonal is 9√2 cm.
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44)
Jan 12, 26 06:35 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 44) -
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations
Jan 07, 26 01:53 PM
US Common Core K-12 Curricum Algebra Solving Simple Equations -
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4)
Jan 05, 26 06:56 PM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 4)
