PRACTICAL PROBLEMS ON RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS IN SET THEORY
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Problem 1 :
An open box is to be made from a square piece of material, 24 cm on a side, by cutting equal squares from the corners and turning up the sides as shown. Express the volume V of the box as a function of x.
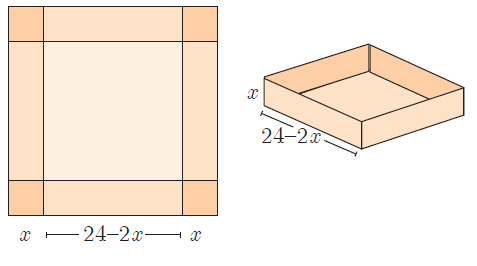
Solution :
Since the original shape is square, length of all sides will be equal.
length = width = 24 - 2x
height = x
Volume of cuboid = length ⋅ width ⋅ height
= (24 - 2x) ⋅ (24 - 2x) ⋅ x
= x(24 - 2x)2
= x [242 - 2(24) (2x) + (2x)2]
= x [576 - 96x + 4x2]
V (x) = 4x3 - 96x2 + 576x
Hence the volume of the cuboid is 4x3 - 96x2 + 576x.
Problem 2 :
A function f is defined by f (x) = 3−2x . Find x such that f (x2) = (f (x))2 .
Solution :
Given that :
f (x) = 3 − 2x
f (x2) = 3 − 2x2 ------(1)
(f (x))2 = (3 − 2x)2
= 32 - 2(3)(2x) + (2x)2
(f (x))2 = 9 - 12x + 4x2 ----(2)
(1) = (2)
3 − 2x2 = 9 - 12x + 4x2
4x2 + 2x2 - 12x + 9 - 3 = 0
6x2 - 12x + 6 = 0
x2 - 2x + 1 = 0
(x - 1)2 = 0
x - 1 = 0 (or) x - 1 = 0
x = 1 (or) x = 1
Problem 3 :
A plane is flying at a speed of 500 km per hour. Express the distance d travelled by the plane as function of time t in hours.
Solution :
Time = Distance / speed
Speed of plane = 500 km per hour
Distance travelled = d
time taken = t in hours
t = d/500
d = 500t
Hence the required distance is 500 t.
Problem 4 :
The data in the adjacent table depicts the length of a woman’s forehand and her corresponding height. Based on this data, a student finds a relationship between the height (y) and the forehand length(x) as y = ax +b , where a, b are constants.
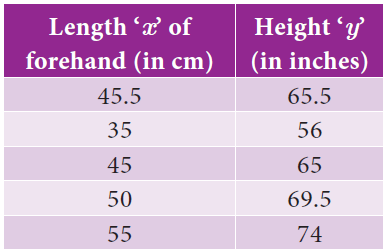
(i) Check if this relation is a function.
(ii) Find a and b.
(iii) Find the height of a woman whose forehand length is 40 cm.
(iv) Find the length of forehand of a woman if her height is 53.3 inches.
Solution :
y = ax + b
(i) For every values of x, we get different values of y.Hence it is a function.
(ii)
|
y = a x + b x = 45.5, y = 65.5 65.5 = a(45.5) + b 65.5 = 45.5 a + b --(1) |
y = a x + b x = 35, y = 56 56 = a(35) + b 56 = 35 a + b --(2) |
By solving these two equation, we get a and b
(1) - (2)
(45.5 a + b) - (35a + b) = 65.5 - 56
45.5 a - 35a + b - b = 9.5
10.5a = 9.5
a = 9.5/10.5
a = 0.90
Substitute a = 0.90 in (1),
45.5(0.90) + b = 65.5
b = 65.5 - 40.95
b = 24.5
y = 0.9x + 24.5
(iii) Find the height of a woman whose forehand length is 40 cm.
y = ? if x = 40
y = 0.9(40) + 24.5
y = 60.5
Height of woman is 60.5 inches.
(iv) x = ? if y = 53.3
53.3 = 0.9x + 24.5
53.3 - 24.5 = 0.9x
28.8/0.9 = x
x = 32
Length of forehand is 32 inches.
Problem 5 :
If R(x) = (2x - 3) / (x + 2)
a) Evaluate i) R(0) ii) R(1) iii) R(-1/2)
b) Find the value of x, where R(x) does not exists.
c) Find R(x - 2) in simplest form.
d) Find x, if R(x) = -5
Solution :
Given that, R(x) = (2x - 3) / (x + 2)
i) R(0)
If x = 0
R(0) = (0 - 3) / (0 + 2) ==> -3/2
ii) R(1)
If x = 1
R(1) = (2 - 3) / (1 + 2) ==> -1/3
iii) R(-1/2)
If x = -1/2
R(-1/2) = (-1 - 3) / ((-1/2) + 2) ==> -4 / (3/2)
= -8/3
b) R(x) will become does not exists, when the denominator becomes 0
When x = -2, x + 2 will become 0.
c) To find R(x - 2), we have to apply x as x - 2 in the given function.
R(x) = (2(x - 2) - 3) / (x - 2 + 2)
= (2x - 4 - 3) / x
= (2x - 6) / x
d) Find x, if R(x) = -5
When R(x) = -5
-5 = (2x - 3) / (x + 2)
-5(x + 2) = 2x - 3
-5x - 10 = 2x - 3
-5x - 2x = -3 + 10
-7x = 7
x = -1
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
Recent Articles
-
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 40)
Dec 18, 25 08:49 AM
10 Hard SAT Math Questions (Part - 40) -
Specifying Units of Measure
Dec 15, 25 07:09 PM
Specifying Units of Measure -
Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers
Dec 14, 25 06:42 AM
Quantitative Reasoning Questions and Answers
