TANGENT LINES TO CIRCLES
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
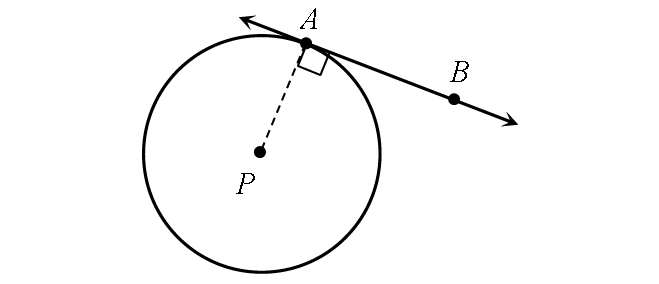
A tangent line intersects a circle at exactly one point, called the point of tangency.
A line is tangent to a circle if and only if it is perpendicular to a radius drawn to the point of tangency.
Solved Examples
Example 1 :
Determine if the line segment AB is tangent to circle P.
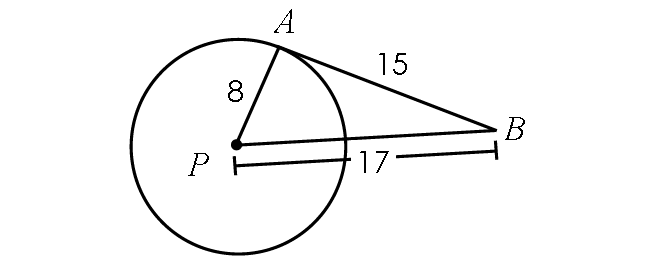
Solution :
If the line segment AB is tangent to circle P, it is perpendicular to the radius PA.
Then, m∠PAB = 90° and triangle PAB has to be a right triangle.
Using Pythagorean Theorem, verify whether triangle PAB is a right triangle.
PA2 + PB2 = PB2
82 + 152 = 172 ?
64 + 225 = 289 ?
289 = 289 ?
The above result is true.
So, triangle PAB is a right triangle and m∠PAB = 90°.
Hence, the line segment AB is tangent to circle P.
Example 2 :
Determine if the line segment YX is tangent to circle Z.
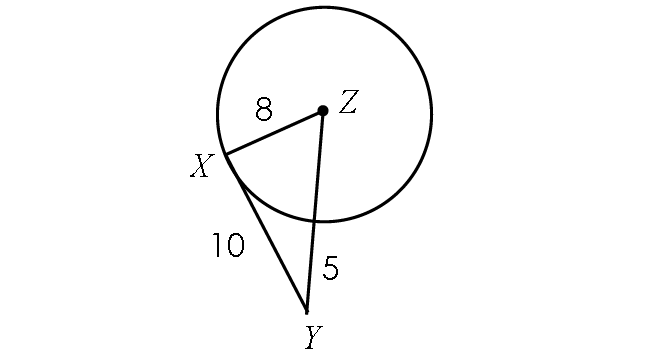
Solution :
Find the length of ZY :
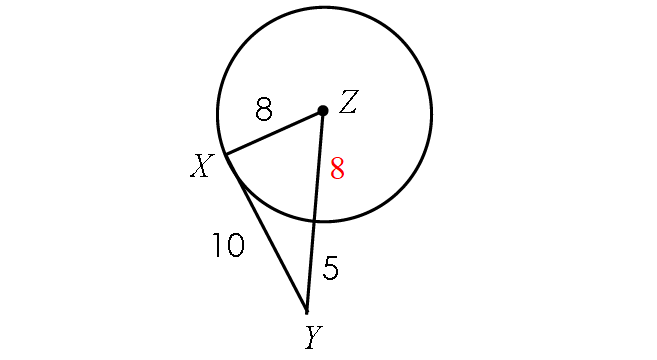
ZY = Radius + 5
ZY = 8 + 5
ZY = 13
Because the line segment YX is tangent to circle Z, it is perpendicular to the radius ZX.
Then, m∠ZXY = 90° and triangle ZXY has to be a right triangle.
Using Pythagorean Theorem, verify whether triangle ZXY is a right triangle.
ZX2 + XY2 = ZY2
82 + 102 = 132 ?
64 + 100 = 169 ?
164 = 169 ?
The above result is false.
So, triangle ZXY is not a right triangle and m∠ZXY ≠ 90°.
Hence, the line segment YX is not tangent to circle Z.
Example 3 :
If the line segment JK is tangent to circle L, find x.
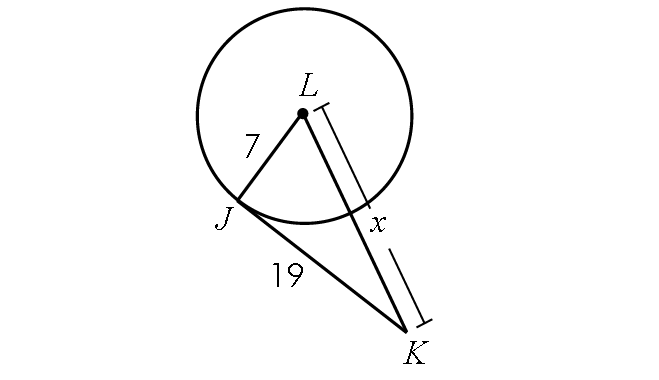
Solution :
Because JK is tangent to circle L, m∠LJK = 90° and triangle LJK is a right triangle.
BY Pythagorean Theorem,
LJ2 + JK2 = LK2
72 + 192 = x2
49 + 361 = x2
49 + 361 = x2
400 = x2
Take square root on both sides.
20 = x
Example 4 :
If the line segment JK is tangent to circle L, find x.
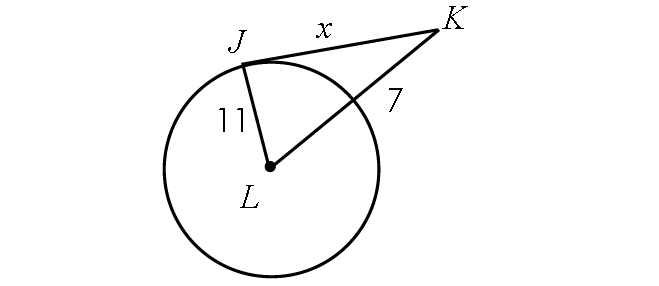
Solution :
Find the length of LK :
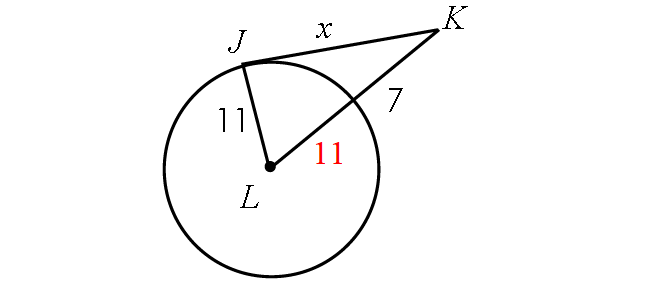
LK = Radius + 7
LK = 11 + 7
LK = 18
Because JK is tangent to circle L, m∠LJK = 90° and triangle LJK is a right triangle.
BY Pythagorean Theorem,
LJ2 + JK2 = LK2
112 + x2 = 182
121 + x2 = 324
Subtract 121 from each side.
x2 = 203
Take square root on both sides.
x ≈ 14.2
Example 5 :
If the line segment JK is tangent to circle L, find x.
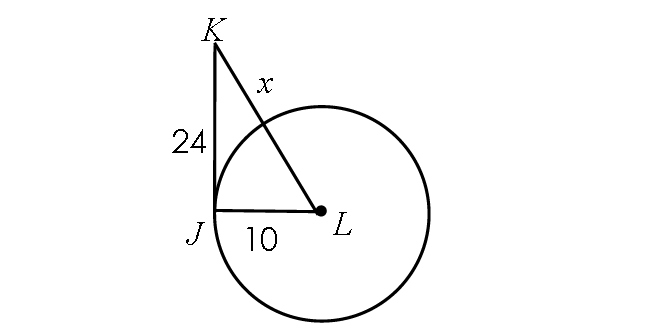
Solution :
Find the length of LK :
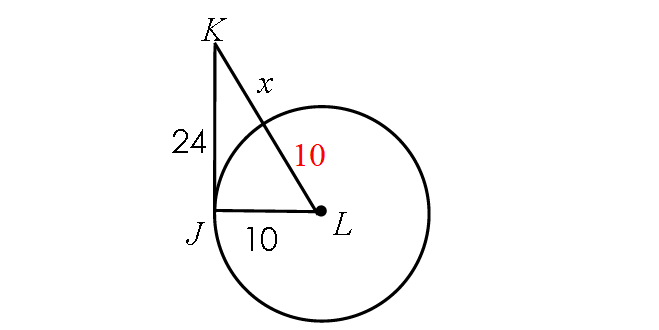
LK = Radius + x
LK = 10 + x
Because JK is tangent to circle L, m∠LJK = 90° and triangle LJK is a right triangle.
BY Pythagorean Theorem,
LJ2 + JK2 = LK2
102 + 242 = (10 + x)2
676 = (10 + x)2
Take square root on both sides.
26 = 10 + x
Subtract 10 from each side.
16 = x
Example 6 :
If the line segment JK is tangent to circle L, find x.
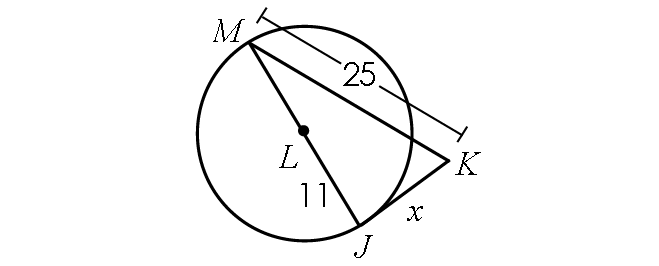
Solution :
Find the length of JM :
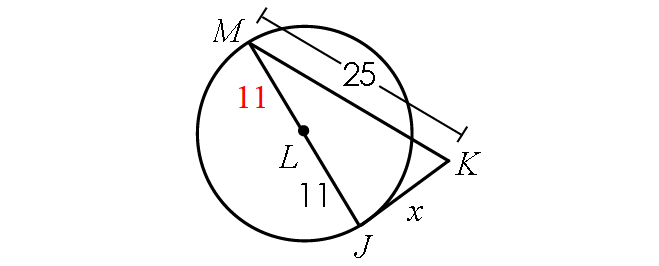
JM = JL + LM
JM = 11 + 11
JM = 22
Because JK is tangent to circle L, m∠MJK = 90° and triangle MJK is a right triangle.
BY Pythagorean Theorem,
JM2 + JK2 = MK2
222 + x2 = 252
484 + x2 = 625
Subtract 484 from each side.
x2 = 141
Take square root on both sides.
x ≈ 11.9
Subscribe to our ▶️ YouTube channel 🔴 for the latest videos, updates, and tips.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
About Us | Contact Us | Privacy Policy
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com

Recent Articles
-
SAT Math Practice Hard Questions
Feb 16, 26 08:56 AM
SAT Math Practice Hard Questions -
SAT Math Preparation with Hard Questions
Feb 16, 26 08:15 AM
SAT Math Preparation with Hard Questions -
SAT Math Practice Problems with Answers
Feb 16, 26 07:53 AM
SAT Math Practice Problems with Answers

